Investments in
Equity Securities
Presentations for Chapter 8 by Glenn Owen
Key Points
Criteria that must be met before a security can be listed in
the current assets section of the balance sheet.
Trading and available-for-sale securities and how the markto-market rule is used to account for them.
Why companies make long-term investments in equity
securities.
The mark-to-market method, the cost method, and the equity
method of accounting for long-term equity investments, and
the conditions under which each method is used.
Consolidated financial statements, when they
are prepared, and how they differ from
financial statements that account for equity
investments using the equity method.
Equity Securities
Classified as Current
Existence of a ready market
– Readily marketable meaning that a security can be sold
and converted into cash on demand
Intention to convert
Trading and
Available-For-Sale Securities
Purchasing trading and available-for-sale
securities
Declaration and receipt of cash dividends
Sale of securities
Price changes of securities on hand at the end of
the accounting period
Reclassifications and permanent
market value declines
Mark-to-market accounting and
comprehensive income
Purchasing Trading and
Available-for-sale Securities
Trading Securities
Available-for Sale Securities
Cash
Dr.
xxx
xxx
Purchased trading and available-for-sale
securities for cash.
Cr.
xxx
Declaration and Receipt of
Cash Dividends
Dividends Receivable
Dividend Income
Recognize declaration of dividend.
Cash
Dividend Receivable
Recognize declaration of dividend.
Dr.
xxx
Cr.
xxx
xxx
xxx
Sale of Trading Securities
Dr.
xxx
Cr.
Trading Securities
Realized Gain on Sale of Trading Securities
Sold trading securities for a gain
or
Cash
xxx
Realized Loss on Sale of Trading Securities
xxx
Trading Securities
Sold trading securities sold for a loss
xxx
xxx
Cash
xxx
Sale of
Available-for-Sale Securities
Cash
Available-for-Sale Securities
Realized Gain on Sale of
Available-for-Sale Securities
Sold available-for-sale securities for a gain
or
Cash
Realized Loss on Sale of
Available-for-Sale Securities
Available-for-Sale Securities
Sold available-for-sale securities for a loss
Dr.
xxx
Cr.
xxx
xxx
xxx
xxx
xxx
Price Changes of Securities On
Hand at the End of the Period
Dr.
Trading Securities
xxx
Unrealized Gain on Trading Securities
Revalued trading securities to market
or
Unrealized Loss on Trading Securities
xxx
Trading Securities
Revalued trading securities to market
Cr.
xxx
xxx
Price Changes of Securities On
Hand at the End of the Period
Dr.
xxx
Available-for-Sale Securities
Unrealized Gain on
Available-for-Sale Securities
Revalued available-for-sales securities to market
or
Unrealized Loss on
Available-for-Sale Securities
xxx
Available-for-Sale Securities
Revalued available-for-sales securities to market
Cr.
xxx
xxx
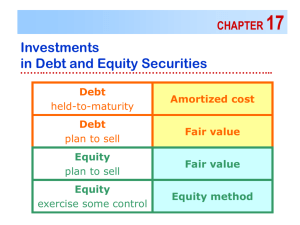
Long-Term Equity Investments
The cost method
– Market value is indeterminable
– Ownership is less than 20 percent
– No change is made in the carrying value of the investment
The equity method
– Significant influence (20 - 50 percent ownership)
– Periodically increase(decrease) the carrying value of the
investment by the investor’s proportionate
share of the net income (loss) of the investee.
– Decrease the carrying value of the investment
by dividends received.
Long-Term Equity Investments
Equity method cautions
– This method will give rise to a difference between
reported net income (loss) and cash flow from
operations.
– It ignores market price.
– 20-50 percent is not always a valid indication of
significant influence.
– It generates off-balance sheet financing
Consolidated financial statements
– Greater than 50 percent ownership
– Purchase or pooling methods
Accounting for Equity Securities
Marketable?
Intend to
liquidate within
time period of
current assets?
Yes
Yes
Proportion of
voting shares
Accounting Mark-toTreatment
Market
No
<20%
Mark-toMarket
20-50%
>50%
Equity ConsoliMethod
date
Accounting for Equity Securities
Marketable?
No
Intend to
No
liquidate within
time period of (implied)
current assets?
Proportion of
voting shares
Accounting
Treatment
No
<20%
Cost
Method
20-50%
>50%
Equity ConsoliMethod
date
Goodwill Accounting Controversy
Goodwill is defined as the excess amount paid for
a corporation over the fair market value of the
acquired company’s assets and liabilities.
Goodwill appears on the balance sheet.
Until recently, goodwill was amortized over a
future period not to exceed forty years.
In July 2001, the FASB passed an accounting
standard with removes the requirement
to amortize goodwill.
Review Problem I (a)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
$170
350
150
MV - Cost
$30
(25)
30
Mark-to-market journal entry on 12/31/xx for AAA:
Trading Securities (AAA) (+A)
30
Unrealized Gain on Trading Securities(R, +SE) 30
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
Review Problem I (a)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
$170
350
150
MV - Cost
$30
(25)
30
Mark-to-market journal entry on 12/31/xx for BBB:
Unrealized Loss on Trading
Securities (Lo, -SE)
Trading Securities (BBB) (-A)
25
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
25
Review Problem I (a)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
$170
350
150
MV - Cost
$30
(25)
30
Mark-to-market journal entry on 12/31/99 for CCC:
Available-for-Sale Securities (CCC) (+A)
Unrealized Loss on
Available-for-Sale Securities (+SE)
30
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
30
Review Problem I (b)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
$170
350
150
MV - Cost
$30
(25)
30
Sold all of AAA in 2000 for $180:
Cash (+A)
180
Trading Securities (-A)
170
Realized Gain on Trading Securities (Ga, +SE) 10
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
Review Problem I (b)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
$170
350
150
Sold 20% of BBB in 2000 for $65:
MV - Cost
$30
(25)
30
20%
Cash (+A)
65
Realized Loss on Trading Securities (Lo, -SE 5
Trading Securities (-A)
70
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
Review Problem I (b)
Securities
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
Cost
Market Value
$140
375
120
MV - Cost
$170
350
150
$30
(25)
30
Received $60 in BBB dividends and $30 in
dividends were declared on CCC stock:
Cash (+A)
Dividends Receivable (+A)
Dividend Revenue (R, +SE)
60
30
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
90
Review Problem I (b)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
MV - Cost
$170
350
150
$30
(25)
30
Revalued BBB shares to market 12/31/00:
Unrealized Loss on
Trading Securities (Lo, -SE)
Trading Securities (BBB) (-A)
40
$2 per share x 20 shares.
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
40
Review Problem I (b)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
MV - Cost
$170
350
150
$30
(25)
30
Revalued CCC shares to market 12/31/00:
Unrealized Price Increase
on Available-for-Sale Securities (-SE)
Available-for-Sale Securities (CCC) (-A)
15
$1 per share x 15 shares.
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
15
Review Problem I (c)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
MV - Cost
$170
350
150
$30
(25)
30
Sold 20 shares of BBB stock during 2001:
Cash (+A)
Trading Securities (BBB) (-A)
Realized Gain on
Trading Securities (R, +SE)
Gain of $1 per share x 20 shares.
260
240
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
20
Review Problem I (c)
Securities
Cost
*AAA
*BBB
**CCC
$140
375
120
Market Value
MV - Cost
$170
350
150
$30
(25)
30
Sold 15 shares of CCC stock during 2001:
Cash (+A)
Unrealized Gain on
Available-for-Sale Securities (-SE)
Available-for-Sale Securities (CCC) (-A)
Realized Gain on
Available-for-Sale Securities (Ga, +SE)
165
15
* Trading security ** Available-for-sale security
135
45
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2003, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in
Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the
express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
Request for further information should be addressed to the
Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser
may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for
distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility
for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these
programs or from the use of the information contained herein.