Guided Notes – Macromolecules Name: Objectives Identify
advertisement

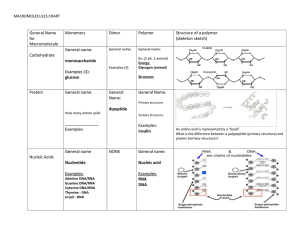
GUIDED NOTES – MACROMOLECULES Name:______________________________________________ Objectives Identify macromolecule type from pictures or models Describe the functions of macromolecules Identify examples of the four macromolecules found in the human body Macromolecules are large organic molecules that consist of chains of repeating subunits called ___________________________. Macromolecule Monomer Saccharides Fatty acids (sort of) Amino acids Nucleotides Carbohydrates All have the formula: _______________________________ Classified as: ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ Function in humans: ___________________________________ Monosaccharide examples: Glucose______________________________________________________________ Ribose _______________________________________________________________ 1 glucose Disaccharide example Lactose __________________________________________________________ Polysaccharide example Glycogen ___________________________________________________________ Lipids Diverse, but all are non-polar (thus hydrophobic) What does this mean??? 2 Type Function Triglycerides (fats & Oils) Steroids (including cholesterol) Phospholipids Vitamins (A, E, K) Energy storage – lipids vs carbs LIPIDS Usually long-term More energy dense Cannot be easily transported Doesn’t impact osmotic balance Less easily digested Carbs Usually short-term Less energy dense Can be transported Impacts osmotic balance More easily digested Proteins 3 Proteins are complexly folded chains of amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids which can be arranged in any order, leading to an incredible diversity of structure. Function Example Details Enzymes Breaks down lactose Movement Slide past each other to cause muscle contraction Transport Carries oxygen in blood Structural Tough fiber that provides strength Hormones Regulates blood sugar Defense Antibodies 4 Nucleic Acids DNA: Genetic Information RNA: Transcribes and translates DNA to make proteins Each nucleotide has three parts: A phosphate group A sugar A nitrogenous base (A, C, T, or G) ATP – the energy currency of the cell 5 6