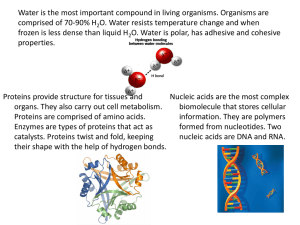
Biochemistry of Food: Macromolecules Answer Key
advertisement
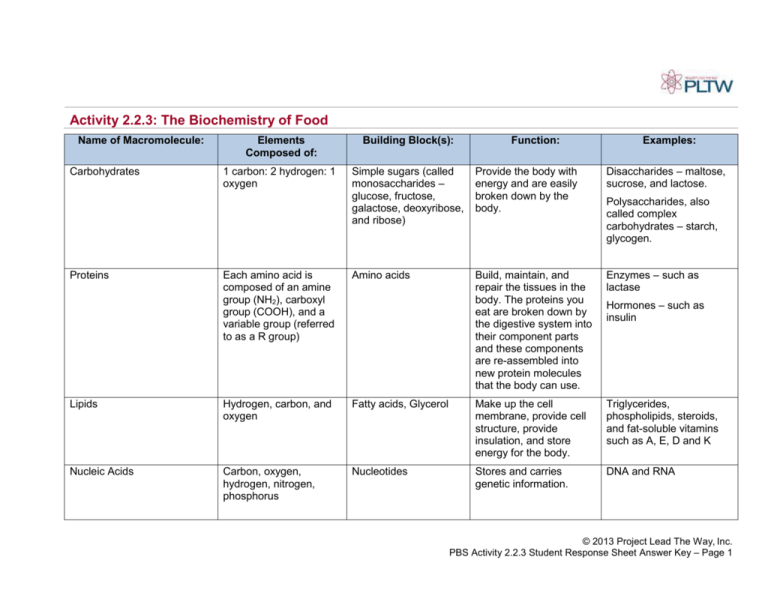
Activity 2.2.3: The Biochemistry of Food Name of Macromolecule: Elements Composed of: Building Block(s): 1 carbon: 2 hydrogen: 1 oxygen Simple sugars (called monosaccharides – glucose, fructose, galactose, deoxyribose, and ribose) Provide the body with energy and are easily broken down by the body. Disaccharides – maltose, sucrose, and lactose. Each amino acid is composed of an amine group (NH2), carboxyl group (COOH), and a variable group (referred to as a R group) Amino acids Build, maintain, and repair the tissues in the body. The proteins you eat are broken down by the digestive system into their component parts and these components are re-assembled into new protein molecules that the body can use. Enzymes – such as lactase Lipids Hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen Fatty acids, Glycerol Make up the cell membrane, provide cell structure, provide insulation, and store energy for the body. Triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, and fat-soluble vitamins such as A, E, D and K Nucleic Acids Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus Nucleotides Stores and carries genetic information. DNA and RNA Carbohydrates Proteins Function: Examples: Polysaccharides, also called complex carbohydrates – starch, glycogen. Hormones – such as insulin © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PBS Activity 2.2.3 Student Response Sheet Answer Key – Page 1 © 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. PBS Activity 2.2.3 Student Response Sheet Answer Key – Page 2