Building Blocks of Cells
advertisement

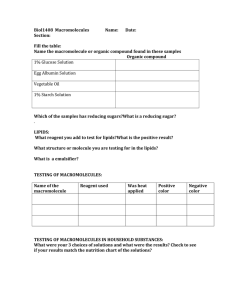
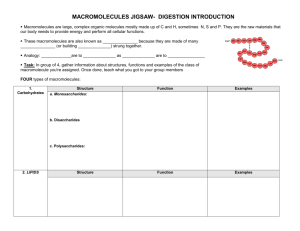
Warm-up 1/31/12 • Teach the Teacher: What is the best kind of candy to get at the gas station? • • Review: What are the three parts of an experiment. • • Learning Target: Defend Whether something is alive or not. • Identify the 4 types of macromolecules. Flash Card • On the Front Write: • Characteristics of Life • On the Back write: • Made of cell (s) • Organization • Grows • Reproduces • Responds to stimuli • Requires energy • Homeostasis • Has adaptations Building Blocks of Cells Science Biology Life Cells Macromolecules • Macro=large • Molecules=two or more atoms bonded together, like H20 • Tons of repeating molecules bonded together to make…macromolecules • Think of them like the wood for building the framing of a house 4 types of Macromolecules • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids Just like there are different materials used to make a house…different materials to make a cell. Carbohydrates • Store energy ▫ Sucrose, lactose, glucose • Provide structural support ▫ Cellulose makes cell wall of plants ▫ Chitin is hard outer layer in the hard outer shell of shrimp, lobsters, and some insects • Made up of carbon and hydrogen • Make up fats, oils, waxes ▫ Coated on leaves (wax) ▫ Beeswax for honeycomb • Store Energy • Provide Barriers for cells ▫ Phospholipids • Include steroids and cholesterol Lipids Lipids • Good lipids (fats) ▫ Saturated fats • Not so good lipids (fats) ▫ Unsaturated fats • Saturated refers to the number of hydrogens that can fit on the macromolecule Proteins • Made of small carbon compounds • Made of amino acids ▫ Think DNA • Used in every function of your body! • 10,000 different proteins Proteins • Transport substances • Speed Reactions • Provide structural support • Make hormones Nucleic Acids • Store and communicate genetic information • made of carbon, nitrogren, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen atoms Notes To Notes Card • Write your name and period on the note card, and use your notes to answer the following questions: 1. What are the four main macromolecules? 2. Which macromolecules provide structural support? 3. What is a macromolecule? 4. Which fat is the good kind of fat? 5. What type of macromolecule is used for barriers, like in honeycomb?