Review of Macromolecules
advertisement

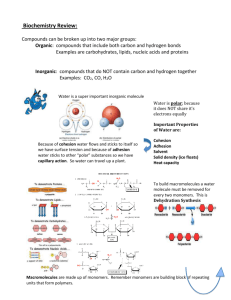
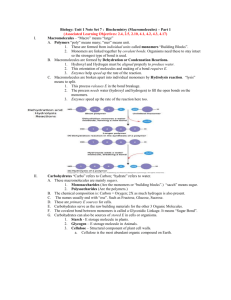
Review of Macromolecules Each box contains several terms. In the blank space to the side, use all of the terms in a couple of sentences. Pretend that you are explaining these words to someone who is totally unfamiliar with them. Carbohydrates, polysaccharide, dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis, monosaccharide Lipids, cholesterol, saturated, unsaturated, fatty acids, phospholipids, glycerol Proteins, peptide bond amino acid, polypeptide BONUS: enzyme, substrate, catalyst, active site Nucleic acids, ribonucleic acid, nucleotides, deoxygribonucleic acid Be A Chemistry Detective: In each of the following exercises you have clues about a compound. Using your knowledge of macromolecules and deductive abilities, identify the molecule. Be as specific as possible. 1._______________: A polysaccharide. Animals store their excess fat in this form. 2._______________: Important in regulating chemical pathways, synthesizing materials needed by cells, and releasing energy. Speed up chemical reactions by binding to reactants. 3._______________: Complex molecules composed of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and phosphorous atoms. Polymers of molecules built up from a special 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogeneous base. 4._______________: A polysaccharide. Gives strength and rigidity to plants. 5._______________: Consist of parts that dissolve well in water and parts that do not dissolve well in water. Form liposomes when mixed with water. 6._______________: All have similar chemical structure but differ in a region known as the R group. Can be joined by polymerization to form proteins. 7._______________: A polysaccharide. Plants store excess sugar in this form. 8._______________: Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in an approximate ratio of 1:2:1. Has the formula of C6H12O6. 9._______________: Long chains of hydrogen and carbon atoms that have a carboxyl group attached at one end. Combine with glycerol to form lipids. 10.______________: A disaccharide. Other examples are maltose and lactose. Write each item below the correct heading: Sucrose glucose C6H12O6 cellulose glycogen starch lactose fructose C12H22O11 Put the terms to the right under the box with the Appropriate heading Monosaccharide Dissacharide Polysaccharide Complete the table by checking the correct column for each description: May check more than one box if the description applies to more than one molecule. Description Made up of nucleotides Lipids Proteins Most consist of three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol molecule DNA and RNA Contain peptide bonds Produce proteins Commonly called fats and oils Made up of amino acids Used for long-term energy storage, insulation, and protective coatings Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen In a short paragraph below: Describe four reasons the structure of carbon allows it to function as a building block for living things. Sketch each of the examples of macromolecules listed below and fill in the table: Nucleic Acids Example DNA Sketch Glucose Amino Acid Triglyceride Structure Meets Function: Category Monomer Polymer Function In the space below, describe what is meant by the statement “structure meets function.” In the boxes below, choose a category of macromolecules and identify how structure meets function within that category of macromolecules. You should use specific examples within your discussion.