Prenatal development and birth
advertisement

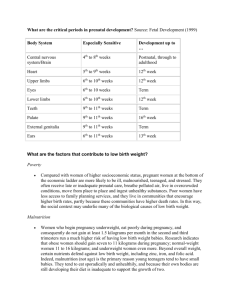
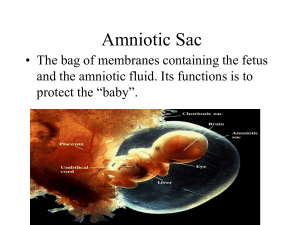
Prenatal development and birth The course of prenatal development periods Germinal First 2 weeks after the conception. events • creation of the zygote, continued cell division and the attachment of the zygote to the uterine wall (Implantation) • blastocyst, the inner cell layer develops. • trophoblast, the outer cell layer develops. It provides the nutrition and support for the embryo. Embryonic 2-8 weeks after conception. • rate of cell differentiation intensifies, support system for cell forms, and organs appear. • zygote becomes the embryo. • blastocyst becomes the endoderm, which will develop into digestive and respiratory system. • trophoblast divides in two parts, i.e. ectoderm, the outer most layer and mesoderm, the middle layer. • ectoderm will become the nervous system, sensory receptors, and skin parts. • mesoderm will become the circulatory system, bones, muscles, excretory and reproductive system. • life-support system for the embryo also matures and develops rapidly. (placenta, umbilical cord and amnion- a bag of clear fluid in which the developing embryo floats. Fetal (begins 2 months after conception and lasts for 7 months, on average) By 3 months, moves its limbs, head; opens and close mouth; face, forehead, eyelids, nose and chin are distinguishable. It can be identified as a male or female. By 4 months, arms and leg movements can be felt by mothers. By 5 months, structures of the skins such as toenails and fingernails will be formed. By 6 months, eyes and eyelids are completely formed. Fine layers of hair covers head. Miscarriage and abortion During miscarriage embryo separates from uterine wall and is expelled by the uterus. causes may be due to chromosomal abnormalities, viral or bacterial infections, abnormalities of reproductive tract. In some cases severe trauma can cause spontaneous abortion. Maternal characteristics Mother’s age, nutrition, and emotional states can affect the prenatal development. Infants born to adolescents are often premature and mortality rate of infants is double that of one born to mother’s in their 20s. Babies with down syndrome are rarely born to mothers below 30, but risk is considered higher for the mothers below 18. Nutrition is very important too as children born malnourished mothers are likely to be malformed. Emotional states and stresses during pregnancy leads to physiological changes and production of adrenaline (usually in response to fear), which may restrict the blood flow to the uterine area and may deprive the fetus of adequate oxygen. Maternal anxiety during pregnancy in a study was also associated with infants, who were more hyperactive and irritable along with feeding and sleeping problems. Teratology and hazards to prenatal development The field of study that investigates the causes of birth defects is called teratology. Teratogen is any agent that causes a birth defect. The probability of structural defects is greatest early in the embryonic period. During the fetal period they likely to stunt growth or create problems in the way organs functions. For eg, brain is most vulnerable at 15-25 days after conception, eyes 24-40 days, heart at 24-40 days, and legs at 24-36 days. Maternal diseases and conditions Rubella, syphilis and genital herpes are found to cause death and deformities in children born to mothers who are infected. AIDS Mothers can infect their offsprings -during gestation across the placenta. -during delivery through contact with blood or fluids. -post-partum through breast feeding. Approximately one-third born to infected mothers will ultimately become infected. Babies can be infected and symptomatic or infected but asymptomatic or not infected at all. Drugs Tranquilizers like thalidomide, taken for morning sickness are known to cause devastating effects on fetus. Eg, if a woman takes it on day 26, an arm might not grow. Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a cluster of abnormalities that appear in the offspring of the mothers who drink heavily during pregnancy. Fetal and neonatal deaths are higher among smoking mothers. Studies have also shown that exposure to smoking was related to poor language and cognitive development. Mothers who smoked during pregnancy had infants who were awake more on consistent basis, respiratory problems, and sudden infant death/ crib death were found very common among the offsprings of mothers who smoked during pregnancy. Environmental hazards Radiation can cause gene mutation, an abrupt but permanent change in genetic material. Even radiation from x-rays can affect the fetus. Birth Stages of birth Stage 1 (average of 12-24 hours) Uterine contractions are 15-20 minutes apart and lasts up to 12 hours or more. Contraction comes closer as it progress increases in intensity. It dilates the cervix to an opening of 4” for a baby to move from uterus to birth canal. Stage 2 Head starts to move through the cervix and birth (lasts 1 and half hours) canal. Stage 3 (after birth) Placenta, umbilical cord and other membrane are detached and expelled. Delivery complications Precipitate delivery is a delivery that takes place too rapidly – takes less than 10 minutes to be squeezed through the birth canal. It can disturb infant’s normal flow of blood and the pressure on infant’s head can cause haemorrhaging. if the delivery takes too long, anoxia or the insufficient supply of oxygen to the infant can take place. Anoxia can cause brain damage. The breech position in uterus causes buttocks to emerge first and can cause respiratory problems. Some cannot pass through the cervix and has to be delivered by a cesarean section (surgical removal of the baby from the uterus) The postpartum period The postpartum period is the period after delivery. It is a time when a woman’s body adjusts, both physically and psychologically, having completed the process of childbearing. Physical adjustments o Involution is the process by which the uterus returns to its pre-pregnancy size 5 or 6 weeks after birth. o Nursing the baby helps to contract the uterus at a rapid rate. Emotional and psychological adjustments o Many women undergo a postpartum depression and can have a considerable effect on the infant.