Hazards to Prenatal Development
advertisement

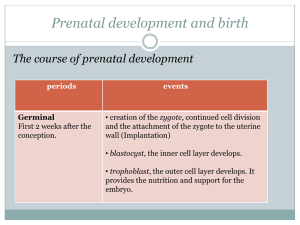
Chapter 2 The Course of Prenatal Development Fertilization to birth Prenatal development lasts approximately 266 days Three periods Germinal Embryonic Fetal The Germinal Period First two weeks after conception Creation of the fertilized egg (the zygote) Cell division Attachment of the zygote to the uterine wall Blastocyst -- consists of an inner mass of cells that will eventually develop into the embryo Trophoblast -- outer layer of cells that later provides nutrition and support for the embryo Implantation -- the attachment of the zygote to the uterine wall takes place about 10 to 14 days after conception The Embryonic Period Occurs from two to eight weeks after conception Rate of cell differentiation intensifies Begins as the blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall Every body part eventually develops from these three layers endoderm ectoderm mesoderm The mass of cells is an embryo Organogenesis -- the process of organ formation during the first two months of prenatal development organs are especially vulnerable to environmental influences Life-support systems for the embryo develop rapidly Life-Support Systems for the Embryo Amnion -- bag containing a clear fluid in which the developing embryo floats Umbilical cord contains two arteries and one vein and connects the baby to the placenta Placenta consists of a disk-shaped group of tissues in which small blood vessels from the mother and the offspring intertwine but do not join The Fetal Period Fetal period begins two months after conception and lasts for seven months Three months after conception -- fetus is about 3 inches long; weighs about 3 ounces By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs close to a pound At birth, the average American baby weighs 7½ pounds and is about 20 inches long Three Trimesters The germinal and embryonic periods occur in the first trimester The fetal period begins toward the end of the first trimester and continues through the second and third trimesters Viability (the chances of surviving outside the womb) occurs at the beginning of the third trimester About 24-25 weeks after conception The Brain By the time babies are born, they have approximately 100 billion neurons The basic architecture of the brain is assembled during the first two trimesters The third trimester and the first two years of postnatal life are characterized by connectivity and functioning of neurons The neural tube develops out of the ectoderm and forms at about 18 to 24 days after conception Two birth defects related to the failure of the neural tube to close are: Anencephaly Spina bifida Folic acid may prevent neural tube defects The generation of new neurons is called neurogenesis Neuronal migration occurs at 6-24 weeks after conception At about the 23rd prenatal week, connections between neurons begin to form Prenatal Tests Ultrasound sonography non-invasive high-frequency sound waves Fetal MRI Used to obtain more detailed images than ultrasound Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) tiny tissue sample from the placenta is removed and analyzed Amniocentesis sample of amniotic fluid is withdrawn and tested for chromosome or metabolic disorders Maternal blood screening Identifies pregnancies that have an elevated risk for birth defects such as spina bifida and Down syndrome Triple Screen Measures three substances in the mother’s blood If abnormal, ultrasound is performed, then amniocentesis Infertility and Reproductive Technology Approximately 10-15 couples in the United States experience infertility Defined as the inability to conceive a child after 12 months of regular intercourse without conception In vitro fertilization (IVF) 25 to 30 percent of pregnancies achieved by fertility treatments result in multiple births Hazards to Prenatal Development A teratogen is any agent that can potentially cause a birth defect or negatively alter cognitive and behavioral outcomes Drugs Incompatible blood types Environmental pollutants Infectious diseases Maternal stress, advanced maternal and paternal age The dose, genetic susceptibility, and the time of exposure influence both the severity of damage to an embryo or fetus and the type of defect Prescription drugs Antibiotics Antidepressants Hormones Accutane Psychoactive drugs Caffeine Alcohol (Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, FASD) Nicotine Cocaine Methamphetamine Marijuana Heroin Incompatible blood types Difference in blood groups -- A, B, O, and AB Rh factor Environmental hazards Toxic wastes X-ray radiation Maternal diseases Rubella Syphilis, genital herpes, HIV/AIDS Diabetes Other Parental Factors Maternal diet and nutrition Overweight before and during pregnancy Folic acid is important for normal prenatal development Eating fish -- mercury levels Maternal age -- 35 years or older at risk Emotional states and stress Anxiety Depression Paternal factors Smoking Prenatal Care Involves a defined schedule of visits for medical care Provides screening for manageable conditions and treatable diseases Includes comprehensive educational, social, and nutritional services Centering Pregnancy is a new program that is relationship-centered and provides complete prenatal care in a group setting. Childbirth Setting and Attendants In the United States, 99 percent of births take place in hospitals Midwives Practiced throughout the world 95 percent of the midwives who delivered babies in the United States were certified nurse-midwives Doulas A caregiver who provides continuous physical, emotional, and educational support for the mother before, during, and after childbirth Methods of Childbirth Medications Three basic kinds of drugs Analgesia Anesthesia Oxytocics Natural and Prepared Childbirth Natural childbirth -- reduce pain with breathing techniques and relaxation Prepared childbirth -- a.k.a. Lamaze Other Non-Medicated Techniques to Reduce Pain Waterbirth -- giving birth in a tub of warm water likely to be less stressful for the baby and the mother Massage -- reduce pain and anxiety Acupuncture -- insertion of strategically located needles Breech or Cesarean Delivery Breech position -- buttocks rather than head emerge first Can prevent the baby from breathing normally Cesarean delivery -- the baby is removed from the mother’s uterus through an incision made in her abdomen May be lifesaving but carries the risks of major surgery Apgar Scale Used to assess the health of newborns at one and five minutes after birth A score, or reading, of 0, 1, or 2 on each of these five health signs heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, body color, and reflex irritability Anoxia -- an insufficient supply of oxygen Low Birth Weight and Preterm Infants Low birth weight -- less than 5½ pounds at birth Very low birth weight -- under 3 pounds Extremely low birth weight -- under 2 pounds. Preterm -- born three weeks or more before full term Small-for-date -- birth weight is below normal when the length of the pregnancy is considered Incidence and Causes of Low Birth Weight Incidence of low birth weight varies considerably from country to country Related to poverty, maternal health status, maternal nutrition More health and developmental problems than normal-weight infants At school age, more likely to have a learning disability, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, or breathing problems such as asthma Nurturing Low Birth Weight and Preterm Infants Kangaroo care -- a way of holding an infant so that there is skin-to-skin contact for two to three hours per day over an extended time in early infancy Massage therapy -- firm stroking with the palms of the hands three times per day for 15-minute periods Bonding -- formation of a connection, especially a physical bond, between parents and the newborn in the period shortly after birth The Postpartum Period Postpartum period -- lasts for about six weeks after childbirth or delivery or until the mother’s body has completed its adjustment and has returned to a nearly pre-pregnant state Physical and psychological adjustments Involution -- process by which the uterus returns to its pre-pregnant size Emotional and Psychological Adjustments Baby blues -- two to three days after birth, many women begin to feel depressed, anxious, and upset Postpartum depression -- a major depressive episode about four weeks after delivery Fathers also undergo considerable adjustment in the postpartum period, even when they work away from home all day Postpartum Blues and Postpartum Depression Among U.S. Women Pregnancy, Childbirth and Motherhood Prenatal care Pregnancy—9-month sickness What do you know about pregnancy? How is this information known? Pregnancy normal and healthy, although occasionally Physical Reactions During Pregnancy Weight gain; Protrusion of abdomen Breast tenderness Frequent urination Fatigue & nausea Individual differences Interest in Sexual activities Research? uncomfortable and inconvenient Emotional Reactions During Pregnancy---great variation exists between women Positive Emotions wonder and awe—new growing person married women—doing what they are “supposed to” transition into adulthood—sense of accomplishment and purpose sense of attachment anticipation—find pleasure in looking forward to tasks of motherhood and child rearing—and a source of satisfaction Negative Emotions change—emotions fragile and changing depression, fears and anxieties self-image and unattractive—culture that values slimness—woman’s self-image may deteriorate loss of identity—now a “pregnant woman health issues Factors influencing a woman's response to pregnancy physical reaction planned pregnancy relationship with baby's father economic status miscarriage-unintended termination of pregancy Stressful events Attitudes Toward Pregnant Women—pregnancy a public event Situational factors—context shopper or apply for job Hostile and benevolent sexism—pregnant women seen as fragile and dependent, less threatening Attitudes a function of where maternity clothes are located-- Maternity clothes and social status—high status stores: femininity, privacy; low status stores: image of being fat with job to do Research by Shelley Taylor and Ellen Langer 1977: pregnant or not in elevator People tend to avoid standing close to pregnant women, men especially. Both looked furtively looked at stomach People likely to help a pregnant woman Employment during pregnancy Ethnic, class, and cultural differences—black women not expected to stay home full time; developing countries often expected to work Combining career and children—especially if college graduate Typical Work Patterns Employment during pregnancy does not endanger the health of the pregnant woman or the baby Factors Related to Premature Delivery: physically demanding job night shift prolonged standing without a break Emotional Reactions to Childbirth--Wide variation Intense joy Reactions to pain Fathers' reactions—when participate in birth of child, experience intense joy Motherhood Images of mothers and motherhood----Is there a motherhood mystique? Motherhood mandate Stereotypes About Motherhood Contradictory messages of happy fulfillment, perfect mothering, and evil force Stereotype emphasizes that woman’s ultimate fulfillment achieved by becoming a mother Short adjustment, then competent mother, devoted to family. The Reality of Motherhood Negative Factors 1. Child care is physically exhausting; sleep deprivation is also common. 2. Roughly 35% of infants in U.S. are born to unmarried women; mothers may not have adequate income. 3. Fathers help much less with child rearing than mothers had expected. 4. For several weeks after childbirth, women report that they feel leaky and dirty, coping with after-birth discharges. They are also likely to feel pain in the vaginal area, the uterus, and the breasts. 5. New mothers seldom have training for the tasks of motherhood. they often report feeling incompetent. 6. Babies cry much more than parents expect, and they do not smile until they are about 2 months old. In reality, babies do not smile until they are about 2 months old; also, many babies are fussy, and they resist cuddling. 7. Mothers of newborns may have little contact with other adults. 8. The woman’s romantic partner may feel neglected. 9. Women feel disappointed in themselves because they do not match the standards of the ideal mother, the completely unselfish and perfect woman. 10. People frequently blame mothers—more than fathers—for most of the problems that infants and children develop. Infant Mortality Positive factors: Discovering a sense of strength—empowered, confident Interactions with their children—intense loving interaction Children can be fun and interesting Look at world from new viewpoint Develop new aspects of personality----Help parent develop an important part of own personality---ability to nurture When fathers participate and express admiration for their partners, marital satisfaction increases Many mom’s state difficult to describe positive side, more abstract, more intense. Motherhood and Women of Color-- Wide variation of customs across cultures Stereotypes of Black mothers—Black welfare mother & Black superwoman Extended families provide stabilizing influence in Black and Latina/o cultures Continuity of generations emphasized in many North American Indian cultures Lesbian Mothers Diversity of situations Diversity of situations Lesbian mothers and heterosexual mothers have similar parenting styles. Lesbian mom: children raised by lesbians are well adjusted, and do not differ substantially from children raised by heterosexuals. Differences found in gender stereotypes in children—because raised in less traditional setting. Partners likely to equally share financial and family responsibilities. Lesbian mothers and heterosexual mothers have similar parenting styles Lesbian mothers are more likely to engage in imaginative play with their children and less likely to spank them. Most children raised by lesbians are positive about their mothers' relationships Custody and adoption Breast Feeding Education Age Ethnicity Social support Health benefits of breast feeding Postpartum Disturbances Postpartum period Postpartum blues (maternity blues) short-lasting change in mood usually occurs during first 10 days after childbirth experienced by about half of new mothers symptoms include crying, sadness, insomnia, irritability, anxiety, and feeling overwhelmed Postpartum depression (postnatal depression) more serious disorder symptoms include extreme sadness, fatigue, despair, low of interest in enjoyable activities, and loss of interest in the baby affects about 10% to 15% of women who have given birth begins to develop within 6 months after childbirth may last for many months similar to other kinds of depression Social factors stress economic status social support No consistent relationship found between hormonal levels and postpartum disorders Returning to the Workplace After Childbirth Individual differences Length of maternity leave not correlated with mental health measures except for women who consider their employment an important part of their identity Homemakers, women employed part time, and women employed full time have similar mental health measures one year after childbirth. Maternity/Family Leave Policies Deciding Whether To Have Children Attitudes Toward Women Choosing Not to Have Children compulsory motherhood child-free women rated as lower than women with children on fulfillment, happiness and having a rewarding life advice from friends and relatives the number of children Advantages and Disadvantages of Being Child-Free Advantages of Being Child-Free: 1. Parenthood is an irrevocable decision., you can’t take children back to the store for a refund. 2. Some couples are afraid that they will not be good parents. 3. Parenthood is extremely stressful. 4. Some couples realize that they don't have the energy required to raise children. 5. Some couples realize that they genuinely do not enjoy children. 6. Some couples are reluctant to give up a satisfying and flexible lifestyle for a more child-centered orientation. 7. Children can interfere with educational and vocational plans 8. Raising children can be extremely expensive. 9. People can spend time with other people's children, even if they don’t have children of their own. 10.Some couples do not want to bring children into a world threatened by overpopulation, nuclear war, terrorism, and other serious global problems. Reasons for having children 1 Parenthood offers a lifelong relationship of love, connection, nurturance, and social interactions with other human beings, children can enrich people’s lives. 2. Parents have a unique chance to be responsible for someone’s education and training. in raising a child, they can clarify their own values and instill them in their child. 3. Parents can watch their children grow into socially responsible adults and helpe the world become a better place. 4. Parenthood is challenging, it offers people the opportunity to be creative and learn about own potential 5. Through parenting, people can fulfill their relationship with their spouse, and they can become a “family.” 6. Children can be a source of fun, pleasure, and pride. Infertility 10-15% of couples Health and age factors Fertile and infertile women do not differ in their marital satisfaction or self-esteem Many different reactions Infertile women report higher levels of distress and anxiety Caught between hopefulness and mourning Women of color, stereotypes, and racist health care providers Medical treatments and reproductive technologies Many women manage to refocus their lives when infertility seems likely