Handouts for Chapter 4
advertisement

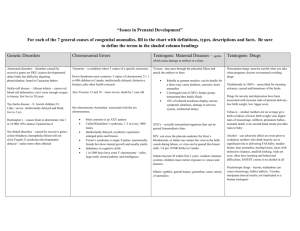
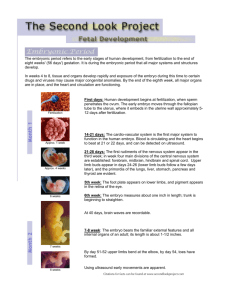
Developmental Psych handouts, Prenatal Devt and Birth 1 Prenatal Development and Birth (1) Germinal Period (conception to implantation, 8-14 days) Zygote blastocyst embryonic disk, trophoblast ►6-10 days after conception, implants into uterine wall ►1 in 4 zygotes survive this phase (2) Period of the embryo (start of 3rd week to end of 8th week) ► formation of major organs, heart starts to beat trophoblast amnion, yolk sac, chorion, allantois placenta: ►barrier to prevent mother’s and embryo’s bloodstreams from mixing ►semi-permeable lets oxygen, carbon dioxide, salts, nutrients pass) ►connects to embryo via umbilical cord (carries oxygen, nutrients to embryo, and removes metabolic waste from embryo) After implantation: ►embryonic disk differentiates into 3 layers of cells 1) ectoderm (hair, skin, nails, oil & sweat glands, nervous system) 2) mesoderm (muscles, bones, connective tissue, circulatory & excretory systems) 3) endoderm (digestive tract, trachea, bronchi, lungs, pancreas, liver) ►after 4th week post-conception, heart is beating, embryo is 10000 times bigger than a zygote ►during 2nd month embryo grows 1/30th of an inch every day, brain develops quickly ►by end of 5ht week, skeleton and limbs are forming, eyes have developed ►by 8th-9th week, sexual development begins” genital ridge (i.e. the “indifferent gonad”) (3) Period of the fetus (9th week til birth, about 7 months) ►major organs start to work ►by end of 3rd month, organs are refined, bones hardening, muscles developing, fetus starts to move limbs, wiggle fingers ►in 2nd trimester (4th, 5th, 6th months) sin thickens, nails harden, eyelashes and hair develop ►by 6th month (25 weeks) auditory and visual systems are functional; fetus is 15 inches long, weighs about 2 lbs ►22nd to 28th week: brain and respiratory system develop; fetus is “viable” ► in third trimester (7th, 8th, 9th months) gain weight (fat), respiratory system strengthens ►by middle of 9th month, fetus is so big that it rests head-down, limbs curled around body (fetal position). Mother has uterine contractions to prepare for childbirth. Environmental Influences on Prenatal Development Maternal Characteristics: ►age: < 15, greater odds of stillborn fetus or later-dying baby; higher odds of dying in childbirth > 35, greater risk of fetal and neonatal deaths, spontaneous abortion ►more than 50% of pregnancies are not planned; an unhappy mother may secrete more adrenaline and other hormones which can affect the fetus ►babies of stressed mothers are fussier, more active, more difficult to feed, to get to sleep, etc. Genetic inheritance? Stress hormones in utero? Field (1985): mothers are more punitive and controlling in child-rearing Developmental Psych handouts, Prenatal Devt and Birth 2 ►Nutrition: mother should gain 25-30 lbs while pregnant malnourished mothers risk congenital defects, long labor, stillbirth, infant mortality in 1st year Teratogen: anything that can harm a developing embryo or fetus leading to deformities, retarded growth, brain damage, or death. ►effects on a particular organ or system are worse when that structure is being formed ►genetic susceptibility ►one teratogens can cause many defects; a single defect can be caused by many teratogens; increased exposure/dose means more serious harm Critical Period: a segment of time in which an organ or system is most sensitive to effects of a teratogens – when it is developing. Defects of head, CNS Heart Other organs, body parts 3rd to 5th week 3rd to mid-6th week 2nd month ►Maternal Diseases rubella in pregnancy: blindness, deafness, cardiac problems, mental retardation - worse in 1st trimester (50-80% affected) - still high in 2nd trimester (13%) syphilis: if untreated, miscarriage is likely, as well as ear, eye, bone, brain damage; worse in middle and later pregnancy herpes (cytomegalovirus, or CMV): blindness, deafness, brain damage, death - most common infectious cause of congenital deafness and mental retardation - genital herpes can cross the placental barrier or be transmitted during childbirth; can lead to blindness, brain damage, 33% of infected neonates die AIDS (HIV infection): 25% of babies with infected mothers are infected. Can get the virus 3 ways: 1) prenatally if virus passes placental barrier 2) during birth, if blood is exchanged as umbilical cord separates from placenta 3) after birth via mother’s milk ► Drugs Thalidomide: a mild tranquilizer prescribed to pregnant women in the 1960s to alleviate morning sickness. Led to thousands of defective children, esp. when taken during 2nd month - deformities of the eyes, ears, nose, hearts, fusion of fingers/toes, phocomelia (parts or entire limbs missing, feet/hands may attach directly to torso) o 21st day: no ears o 25th – 27th day: deformed/missing arms o 28th – 36th day: deformed or missing legs o after 40th day: no effect caffeine: possibly miscarriage, low birth weight, poor motor control oral contraceptives: heart defects Developmental Psych handouts, Prenatal Devt and Birth 3 Diethylstilbestrol (DES): ingredient in a drug used in the 1940s-1960s to prevent miscarriage - DES daughters are at risk for abnormalities of reproductive organs, cervical cancer, miscarriage, early delivery - DES sons are at risk for fertility, immune system problems alcohol: - fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): microcephaly, heart/limb/joint/facial malformation, irritability, hyperactivity, seizures, small size, delayed physical maturation, low IQ, mental retardation - even moderate consumption (1-3 ounces per day) can lead to fetal alcohol effects (FAE): retarded growth, motor skills problems, physical abnormalities, poor attention span, subnormal IQ nicotine: retards rate of fetal growth, increases risk of spontaneous abortion, neonatal death, impairs functioning of placenta - Lefkowitz (1981): long term effects of maternal smoking on 9-11 year olds. Found no differences in size, intelligence, behaviour, popularity. hallucinogens: - heavy marijuana use linked to premature birth, low birth weight - LSD increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, chromosomal abnormalities in offspring narcotics (codeine, heroin, morphine): miscarriage, premature delivery, stillborn - 70-90& of babies born to heroin users are addicted at birth ► Environmental Hazards radiation: mutations, mental retardation, infant death, fetal death zinc, lead, mercury: impaired health and mental abilities, teratogenic effects on fetuses PCBs: smaller, less responsive neonates with long-term memory problems Perinatal Environment: the environment surrounding birth (drugs given during labor and delivery; practices used in delivery; environment after baby is born) 3 stages of childbirth 1st stage (8-14 hours for first-borns, 3-8 hours for later borns): contractions of uterus 10-15 minutes apart, leading to fully dilated cervix 2nd stage (1/2 hour to 1 ½ hours): starts when fetus’ head is at cervical opening - head eventually passes through cervix into vagina - eventually emerges from mother’s body 3rd stage, the afterbirth (5-10 minutes): placenta is expelled from uterus Developmental Psych handouts, Prenatal Devt and Birth Perinatal Hazards: ► Apgar test assesses 5 characteristics: 1. heart rate (0=absent; 1=slow; 2=over 100 beats/minute) 2. respiration (0=absent; 1=slow; 2=good, crying) 3. muscle tone (0=flaccid;1=weak, some flexion; 2=strong, active) 4. colour (0=blue, pale; 1=pink body, blue extremities; 2= completely pink) 5. reflexes (0=no response; 1=frown, grimace, weak cry; 2=vigorous cry, cough, sneeze) poor Apgar scores: ►anoxia (oxygen deprivation) ►positioning of fetus (1 in 10 are breach births, i.e. feet or bottom first; 1 in 500 breach birth babies die at birth or soon after; 2 -4% have cranial bleeding or cerebral palsy) ►forceps can cause cranial bleeding, brain damage ►obstetric medication; up to 9% of mothers are on a drug while giving birth (analgesics, sedatives, stimulants) Brackbill (1985): babies of mothers who were medicated smile less, are irritable/inattentive, hard to comfort or feed Low birth weight: ► preterm infants ►small-for-date infants - more at risk for serious complications Due to mothers’ smoking, drinking, poor nutrition; mothers who are too young; multiple births Short term consequences: ► more than 50% of babies < 1000 grams (2.2 lbs) die at birth or shortly after ►malformations, malnourishment, genetic abnormalities ►respiratory problems due to lack of surfactin (coating on lungs) Long term consequences: ► if in good homes, usually do fine ►if in disadvantaged/ unstable homes, likely to be smaller than other kids, more emotional problems, long-term intellectual deficits 4