Virus & Bacteria Review Answers
advertisement
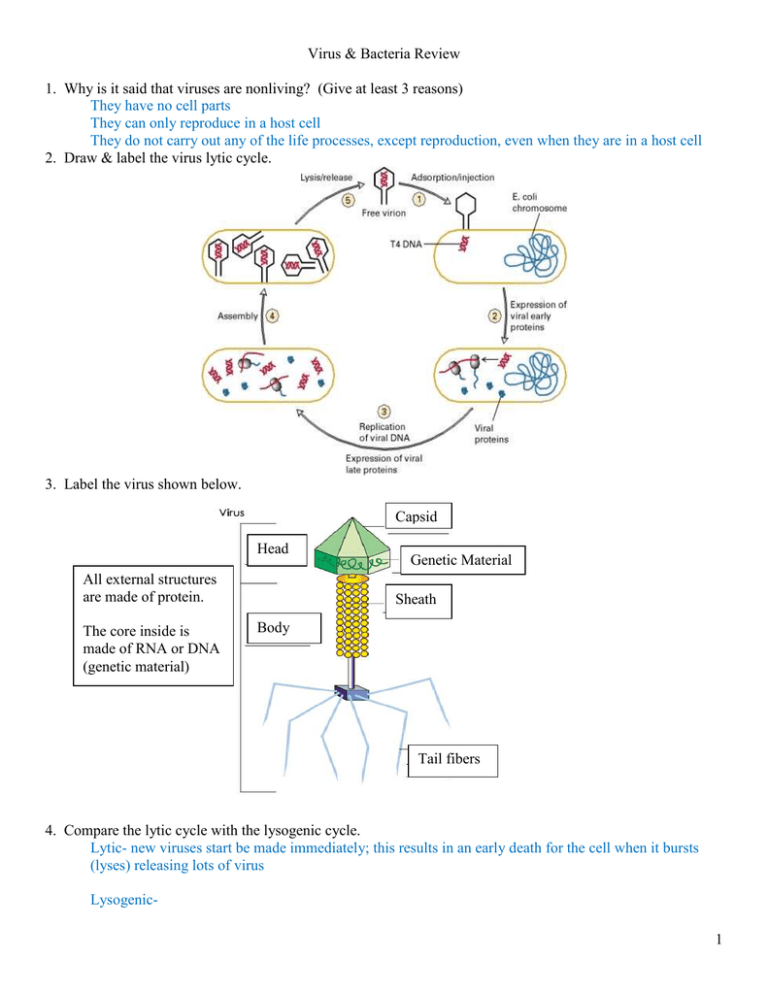
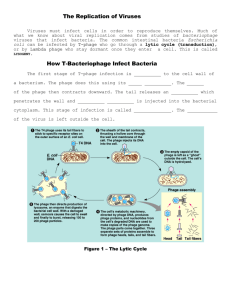
Virus & Bacteria Review 1. Why is it said that viruses are nonliving? (Give at least 3 reasons) They have no cell parts They can only reproduce in a host cell They do not carry out any of the life processes, except reproduction, even when they are in a host cell 2. Draw & label the virus lytic cycle. 3. Label the virus shown below. Capsid Head All external structures are made of protein. The core inside is made of RNA or DNA (genetic material) Genetic Material Sheath Body Tail fibers 4. Compare the lytic cycle with the lysogenic cycle. Lytic- new viruses start be made immediately; this results in an early death for the cell when it bursts (lyses) releasing lots of virus Lysogenic1 5. Compare an RNA virus to a DNA virus. 6. What does our body use to defend us against viruses? 7. What is a vaccine and how does it work? 8. Describe the following viruses. Tell whether they are RNA or DNA viruses, Lysogenic or lytic, and what part of the body they attack. Virus DNA or RNA Lytic/ Lysogenic/ Both Body part or system Influenza Chicken pox Small pox HIV (AIDS) Common Cold 9. Label the parts of the bacterium shown below. 10. Describe bacteria: a. What size are they? Can they be seen with a microscope? b. Do they have membrane bound organelles like eukaryotes do? c. Do they have ribosomes? d. Describe a bacterial chromosome. 2 e. What is a plasmid? f. How do bacteria get around? g. What pH do they like best? h. What is their function? i. How are they harmful to us? j. How are they helpful to us? 11. Compare archaebacteria to eubacteria. 12. How do bacteria make or get food? 13. Define the following a. aerobe b. anaerobe c. facultative anaerobe 14. Compare gram negative bacteria to gram positive bacteria Gram Negative Gram Positive 15. Give two examples of gram positive bacteria 16. Give two examples of gram negative bacteria 17. What are rickettsia and what diseases do they cause? 18. Describe conjugation. How dies it help bacteria? 19. Describe transduction. 3 20. Describe transformation. 21. Draw & label binary fission. What is it used for? 22. What is an endospore and why is it hard to kill? 23. Define the following terms: a. diplob. streptoc. staphylod. coccus e. bacillus f. spirillum 24. Give one example of a bacterial disease caused by the following bacterial types: a. streptococcus b. diphylococcus c. staphylococcus d. streptobacillus 25. What are pili and what are they used for? 26. Describe the Endosymbiotic theory. 4