Bacteria and Viruses
advertisement

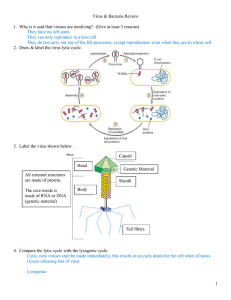
Chapter 19 Lyme disease Tetanus Tuberculosis Bacterial meningitis Strep throat Common cold Influenza AIDS Chicken pox Hepatitis B West Nile Herpes H1N1 Anthrax Botulism Cholera Diphtheria Listeriosis Pneumococcal pneumonia Scarlet fever Syphilis Typhoid fever HPV Measles Infectious mononucleosis Mumps Rabies Rubella SARS Smallpox Viral meningitis Viral pneumonia Gonorrhea Leprosy Pertussis (Whooping cough) Pictures/video Transmission of the pathogen (how it gets into the host) Symptoms (how it affects the host) Treatment (how we “fight” it) Value: Due 20 pts (5 each) date: Wednesday, April 6th at the beginning of class (be ready to present!) Producers: photosynthesis for food chain) Decomposers: (break down/recycle nutrients) Nitrogen fixers: (convert nitrogen gas into “useful” forms for plants and the food chain) Human uses: A) sewage treatment (purifies water, products for fertilizers) B) Food and beverage production C) Digest petroleum (cleaning up small oil spills) D) Make drugs and chemicals through genetic engineering E) Enzymes for medicine Name E. coli is derived from the fact that they live in our colon (large intestine). We give them: A) a warm, safe home B) plenty of food C) free transportation They give us: A) some vitamins we need B) protection from virulent strains of bacteria (see news article) 1. What are two ways bacteria produce disease? 2. What are antibiotics and how do they prevent disease? 3. a) What does the word “virus” mean? b) Describe the events that lead to the study and understanding of viruses. 4. What are the parts of a virus? 5. What are bacteriophages? 6. Draw diagrams of the 2 types of viral infection. (page 481) 7. a) What’s a retrovirus? b) Explain their name. 8. What are vaccines and how do they prevent disease? 1. i) Destroy host cells for food (Ex: tuberculosis). ii) Release of toxins interferes with normal bodily functions (Ex: strep throat, diphtheria). 2.-Compounds that block the reproduction and growth of bacteria; stopping or slowing infection. -Have been responsible for dramatic increases in life expectancy over the last few centuries. Eyes of Nye: Antibiotics 3. a) “Virus” is the Latin word for “poison”. b) –In 1892 farmers’ tobacco plants dying -yellowing pattern (mosaic) on the plant leaves -Disease-causing juice is isolated from plants -Nothing seen in juice under microscope -Some unknown thing (too small to be bacteria) is therefore causing the infection) 4. i) nucleic acid (genes encoded by DNA or RNA) ii) protein coat surrounding the genes, called a capsid 5. Viruses that infect bacteria (“phage” means “eat”) 6. i) Lytic: -Takes over host cell and uses it to make new viral parts (copy itself) - Host cell bursts open, releasing more viruses ii) Lysogenic: -Inserts/incorporates its DNA into host chromosome -This piece of viral DNA is called a provirus -Lies dormant for a while, but then… -At some point, the provirus exits the host chromosome and enters the lytic cycle. Ex: HIV Lysogenic and Lytic Cycles (See page 481 of text) 7. a) RNA is their genetic material (not DNA). b) “Retro” = “backwards”, refers to these viruses doing the reverse of what normally happens. Normal: DNA RNA Protein, but: they go from RNADNA instead. 8. -Preparation of weakened or killed pathogens. -Prompts the body to produce immunity to disease. *See Edward Jenner story (smallpox). Prokaryotes Bacilli Cocci Spirilla Obligate aerobes Obligate anaerobes Facultative anaerobes Binary fission Conjugation Endospore Nitrogen fixation Virus Capsid Bacteriophages Lytic infection Lysogenic infection Prophage Retroviruses Pathogens Vaccine Antibiotics Chemoheterotrophs Photoheterotrophs Photoautotrophs Chemoautotrophs Tobacco mosaic virus E. coli Edward Jenner Using the information on page 482-483, as well as your own opinion, write me a short paragraph telling me whether or not you think viruses should be considered living things or not. Mr. Jessome’s idea of a short paragraph: -More than 2 sentences, but less than 10. Mr. Jessome’s idea of fun: -Writing a short paragraph about whether or not viruses should be considered living things. a) Sterilization by heat: Too hot kills bacteria b) Disinfectants: Chemicals kills bacteria c) Food processing: Cool temps slows bacterial reproduction Antibiotics: -Work for bacterial infections, but not for viruses “anti” = “against” + “biotics” = “living things” Hmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm…. Page 493: #’s 1 -10 (But not #4-You’re welcome) Also: #’s 12, 14, 17, 18, 20, 21, 25 Page 495: #’s 1-5, 7, 8