Organic Chemistry
advertisement

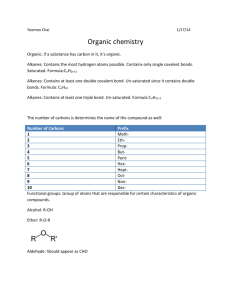
Chapter 22 Organic Compounds All organic compounds contain CARBON. However, not all carbon-containing compounds are classified as organic. Examples: carbonates and oxides are excluded. Carbon-Carbon bonding Carbon atoms are unique in their ability to form long changes and rings of covalently bonded atoms. Can be linked in single, double, or triple bonds. Carbon bonding to other elements. Hydrocarbons-compounds that consist of only hydrogen and carbon. The simplest of the organic compounds Oxygen Nitrogen Sulfur Any Halogen Arrangement of Atoms Due to the bonding capabilities of carbon, many arrangements of atoms can be formed. This effects their properties. They will be completely different. These are called isomers. Example: ethanol and dimethly Structural Formulas We use structural formulas to represent organic compounds. One line-single bond Two lines- double bond Three lines- triple bond Structural Isomers- just the structure form for the two compounds containing the same elements. Geometric Isomers- cis=same side and trans-opposite side Historical Cemistry Read page 715 Hydrocarbons Contain only carbon and hydrogen Prefix # of Carbons meth 1 Eth 2 Prop 3 But 4 Pent 5 Hex 6 Hept 7 Oct 8 Non 9 Dec 10 Alkyl group name methyl ethyl propyl butyl pentyl heptyl heptyl octyl nonyl decyl Alkanes-Saturated Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons containing only single bonds. Use prefixes to name. Prefix ending in ___ane. Count the number of C’s If arranged in a ring or cyclic stucture Cyclo…prefix…ane Branched-Chain Use the longest chain of C’s Look at naming on page 721 CnH2n+2 where n is the number of C’s This can be used to write formulas Properties and Uses of Alkanes Look and table 5 on page 722 Most alkanes exist at room temperature (those that have the lowest molar mass are gases) Natural Gas is a fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon containing from one to 4 carbon chains. Gasoline and Kerosene are mostly liquid alkanes. Paraffin wax-solid alkanes Petroleum- one to 50 carbon’s. Different carbons represent different properties and boiling points. Look at table 6 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons All of the carbons do not have 4 single bonds Alkenes- double bonds CnH2n Rules for naming page 725 Alkynes-triple bonds CnH2n-2 or CnHn Rules for naming page 728 Common name for ethyne is acetylene which is used in welding torches Aromatic Hydrocarbons Six membered carbon rings and delocalized electrons. Benzene is the primary aromatic hydrocarbon. C6H6 Doesn’t behave like alkene’s Look on page 729 for an example of aromatic hydrocarbons Functional groups An atom or group of atoms that is responsible for the specific properties of an organic compound A given functional group undergoes the same types of chemical reactions in every molecule in which it is found. Table 9 on page 731 shows the most common functional groups. Alcohols Used in cold creams, lipsticks, body lotions, alternative fuels, octane enhancers, etc… not just beverages. Not always so good in fuels because the presence of ethanol causes an increased water absorption in fuel. Alkyl Hides The most widely used organic chemicals CFC’s chlorofluorocarbons- used in Freon, also used to make Teflon (nonstick surfaces) Ethers Not very reactive, so commonly used as solvents Aldehydes and Ketones Responsible for odors and flavors Amines All derivatives of ammonia Form from the breakdown of proteins in animal cells Carboxylic Acids Much weaker than inorganic acids Occur naturally in plants and animals Vinegar Citric Acid Benzoic, propanoic, and sorbic acid-preservatives Esters Derivatives of carboxylic acids.