Organic Molecules
advertisement

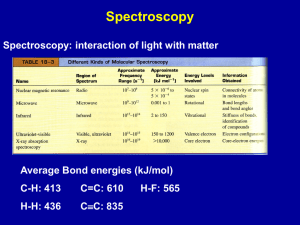
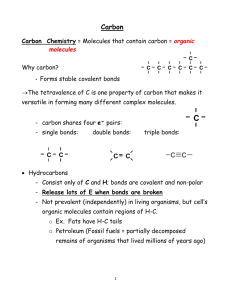
Organic Molecules Chapter 20 Organic Chemistry • Two essential elements are located in column 14 of the periodic table: – Carbon – Silicon • Silicon bonds with four single bonds or less multiple bonds to form the fundamental compounds in the earth. • Carbon similarly bonds in long chains making up essential organic molecules of life. Carbon Bonding • Carbon forms four bonds with itself or other atoms. • More than any other element carbon has the ability to form long chains. • Carbon forms compounds with either single (CH4 Methane), double (C2H4 Ethylene) or triple bonds (C2H2 Acetylene). Shapes of Molecules • Organic molecules follow the rules of VSEPR – Valence – Shell – Electron – Pair – Repulsion Alkanes • Hydrocarbons are compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen • Saturated hydrocarbons have all single bonds on the carbons • Unsaturated hydrocarbons have at least one carbon with a multiple bond (Alkynes and Alkenes) • Hydrocarbons use a simple naming scheme assigned by the number of carbons Isomers • Structural Isomerism occurs when two molecules have the same number of atoms but different bonds. • Butane (C4H10) and all larger Alkanes exhibit structural isomerism. Isomers of Pentane Naming Alkanes Naming Alkanes • Non branched Alkanes are named as in Table 20.1 • Branched hydrocarbons are named by the carbon length of the longest chain. • When an alkyl is substituted for a hydrogen bonded to the carbon; the location, name of substituent, and Alkane are given in the name. Homework • Page 744 –[5-17]