Chapter 19, Section 1
advertisement

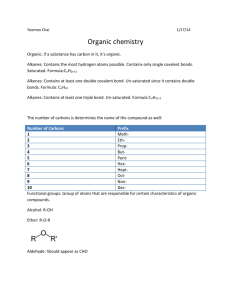
Chapter 19, Section 1, pages 676-686 Carbon and Organic Compounds Compounds of Carbon Objectives To explain the unique properties of carbon To relate different compounds of carbon to their properties To describe the nature of bonds formed by carbon compounds To classify carbon compounds To look at the structure of different isomers of carbon Input Properties of Carbon A plastic water bottle is made of carbon. It is flexible and strong. It is made up primarily of carbon. Carbon atoms always form COVALENT BONDS. Three factors make carbon-carbon bonds unique ------ strong ------carbon not reactive, stable ------each carbon atom can form up to four single bonds Carbon Exists As Different Allotropes An ALLOTROPE is an atom that can form different bonding arrangements. See pg. 679, Fig 2. Diamond = tetrahedral arrangement, graphite = rings but in separate layers, buckminsterfullerene= 60 carbons forming a sphere. All of these compounds are made up only of carbon. Organic Compounds Organic compounds contain carbon. They may also have hydrogen and carbon--then they are called hydrocarbons. Additionally, organic compounds may include N, S, P, and the halogens. Alkanes Are the Simplest Hydrocarbons, CnH2n+2 Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have a straight or branched chain of carbons with only single bonds. The names all end in –ANE. For example, methane CH4, ethane C2H6, propane C3H8. Alkenes. CnH2n This is a hydrocarbon that has one or more double bonds. All end in –ENE. For example, Ethene C2H2, Propene C3H6 Alkynes, CnH2n-2 This is a hydrocarbon that has one or more triple bond. All end in –YNE. For example, ethyne C2H2 (acetylene), propyne C3H4 Carbon Atoms Can Form Rings Carbon atoms can bond in straight chains or in rings. For example, butane C4H10— straight chain or cyclobutane C4H10--- this is a ring of four carbons. Cyclo-means ring or circle. Benzene Is an Important Ring Compound—Aromatic Hydrocarbons The most important ring hydrocarbon is Benzene. Large resonance energy—single and double bonds interchange. Aromatic means have a distinctive odor. Widely used. Found in insecticides, food flavoring, synthetic dyes, etc. Other Organic Compounds Many organic compounds contain functional groups—the portion of a molecule that is active in a reaction and determines the properties of the organic compound. Examples are found on page 684, Table 1 Class Alcohol Aldehyde Ketone Functional Group -OH O=C-H O=C Example propanol Benzealdehyde Propanone (acetone) Use disinfectant Almond flavor Nail polish remover Isomers One of two or more compounds that have the same chemical formula but different structures, C4H10O, 1-butanol, or 2 methyl-1-propanol Conclusion Review key concepts Homework Handout to be given in class