Attachment: Click to download
advertisement

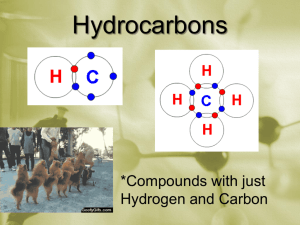
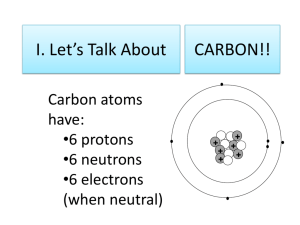
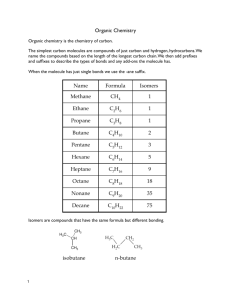
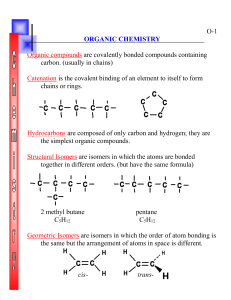
Organic Chemistry Allotropes of Carbon • Allotropes are forms of the same element that have different bonding patterns • Examples: Diamond, Graphite, Amorphous Carbon, Fullerenes (buckyballs) • What makes carbon so special is its half filled valance level and small size. • 4 valance electrons…can bond with a single, double, or triple bond. • Carbon most commonly bonds to itself and then forms long chains and rings. Organic Chemistry • The study of the thousands of carboncontaining compounds. • A general rule an organic molecule is one that contains carbon – Exceptions to that rule are oxides of carbon (CO, CO2) and when you have the carbonate ion CO3-2 Properties of Organic Molecules • They are insoluble in water, have a low melting and boiling point, and form combustion reactions with oxygen. Hydrocarbons • Organic molecules that contain only carbon and hyrdrogen • CH4 C2H6 Properties of Hydrocarbons • HC’s only contain two types of bond C-C or C-H • HC’s have low density, low melting and boiling points, and they don’t dissolve in water Properties of Hydrocarbons • Most hydrocarbons exist deep in deposits of natural gas and petroleum • Both natural gas and petroleum were formed from the compressed and decomposed remains of ancient plants and animals and are called fossil fuels. Hydrocarbons structure and formulas • Carbon atoms in a hydrocarbon can form single, double, or triple bonds and can make straight chains, branched chains, and rings Hydrocarbons structure and formulas • Molecular formula= CH4,C2H6, • Structural Formula= on board • Condensed structural formula=on board Alkanes • Any type of carbon bonding that have only single bonds in them. • 1 carbon 4 hydrogens= Methane • 2 C 6 H = ethane • 3 C 8 H = propane • 4 C 10 H = butane • 5 C 12 H = pentane • 6 C 14 H = hexane • 7 C 16 H = Heptane • 8 C 18 H = Octane • 9 C 20 H = Nonane • 10 C 22 H = Decane