14. organic
advertisement

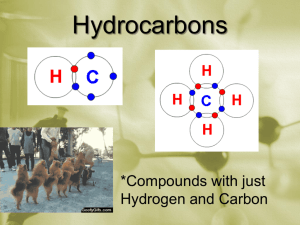
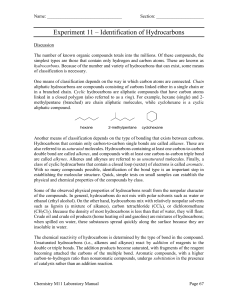
1. Generally non-polar (generally insoluble in water) 2. Soluble in non-polar solvents (likes dissolve in likes ) 3. Non-electrolytes 4. Reactions generally occur slowly 5. Have low melting points due to weak intermolecular forces 6. Reactions have high activation energy, and therefore lower reactions Definition - compounds composed of only hydrogen and carbon Homologous series - group of organic compounds with similar properties and related structures (differ from each other by CH2) Hydrocarbons with the formula CnH2n+2 (Table Q) All alkanes end in “ANE”. Example: methane, ethane, propane All alkanes have all SINGLE bonds and are saturated hydrocarbons. Alkyl structures have one less hydrogen than the corresponding alkane. Side Chain Length In Carbons Name Side chain name Alkyl Formula CnH(2n+2 -1) 1 meth methyl CH3 2 eth ethyl C2H5 3 prop propyl C3H7 4 but butyl C4H9 5 pent pentyl C5H11 6 hex hexyl C6H13 Organic compounds that have the same molecular formula, but different structural formula. The more carbons in the structure, the more isomer variations that are possible. Butane 2-methylpropane Hydrocarbons with the formula CnH2n (Table Q) All alkenes end in “ENE”. Example: ethene, propene All alkenes have at least one DOUBLE bond (C=C) and are considered unsaturated hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons with the formula CnH2n-2 (Table Q) All alkenes end in “YNE”. Example: ethyne, propyne All alkynes have at least one TRIPLE bond (CΞC) and are also considered unsaturated hydrocarbons. Not all organic compounds are hydrocarbons!! Different functional groups cause compounds to have different physical and chemical properties!! Boiling Point/Melting Point The greater the # of carbons in carbon chain, the higher the boiling point/melting point! If compounds have the same # of carbons: Highest BP/MP *Alcohols Ethers *Acids Amines Aldehydes Ketones Lowest BP/MP Hydrocarbons Reactions that involve organic compounds. There are seven (7) reactions we will discuss: Substitution (alkane) Addition (alkene/alkyn) Combustion (carbon comp. + O H O + CO ) Fermentation Esterfication (organic acid + alcohol) Saponification (opp. of esterfication – soap) Polymerization (many small 1 big) 2 2 2