Chemistry Study Guide: Electrons & Periodic Table
advertisement

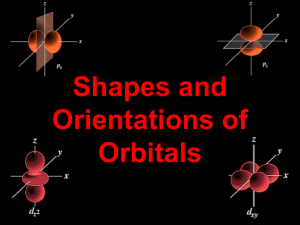
Chemistry Chapter 5 – Electrons in Atoms Study Guide Vocabulary o Atomic emission spectrum o Atomic orbital o Aufbau principle o Electron configuration o Energy level o Ground state o Hund’s rule o o o o o o Pauli exclusion principle Photoelectric effect Photon Principle quantum number Quantum Sublevel-Orbital Objectives o Know the different atomic models associated with Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr and Schrodinger o Understand Einstein and DeBroglie’s contribution to the understanding of the electron o Distinguish between orbits and orbitals o Be able to calculate the number of sublevels, orbitals, and electrons found in each energy level (See table on reference sheet) o Describe how the shapes of orbitals related to different sublevels differ o Know the 3 rules that govern electron configurations o Be able to draw Aufbau diagrams o Be able to write electron configurations (longhand and shorthand) or to identify elements based on their electron configurations o Know the difference between quantum and photon o Be able to use E=h to solve problem o Be able to use c=to solve problem Chemistry Chapter 6 – The Periodic Table Study Guide Vocabulary o Alkali metals o Alkaline earth metals o Anion o Atomic radius (size)/Ionic radius (size) o Blocks on the periodic table o Cation o Electron affinity o Electronegativity o Family o Group o Halogens o Inner transition metals o Ion o Ionization energy o o o o o o o o o o o o Isoelectronic Metalloids Metals Noble gases Nonmetals Outer shell electron configuration (valence electrons) Nuclear charge Nuclear shielding Period Periodic law Representative elements Transition metals Objectives o Explain how elements are organized on the periodic table o Know the contributions of Mendeleev and Moseley o Identify the various types and families of the elements o Describe the information shown by the periodic table o Identify an element based on its electron configuration, period number, group number, family, or periodic trend data o Understand the periodic trends for: Atomic radius / Ionic size Ionization energy Electronegativity/Electron affinity Nuclear charge Nuclear shielding