File

AP Unit 6- Urinary System
Functions:
5
3
4
1
2
6
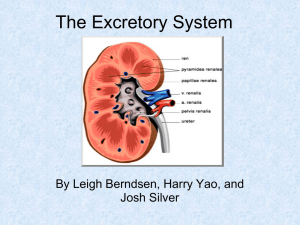
Kidneys – [2]
Location:
Shape –
Size –
External Structures - 3 outer layers
1. renal capsule –
2. adipose capsule –
3. renal fascia –
Internal Structures
Renal Artery-
Renal Vein-
Ureter-
Hilum-
Renal Pelvis-
Name:______________________________________Period___
Label the Diagram below:
Nephrons -
-
-
__________________________________________________________________________________________2_______
3 INNER REGIONS of the Kidney
Pelvis -
Medulla –
Cortex –
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Pyramids -
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
________________________________________________________________________________________3______
Bloods Path through the Kidney
Blood Supply
Renal artery (from abdominal aorta):
Blood flow through nephron
-
-
In Bowman’s Capsule:
-
-
-material is called___________________ and will eventually become _________________
-(blood drainage is by a reverse system, efferent arteriole eventually leads to renal vein - to inf. vena cava.)
Glomerulus has openings ( pores):
B. Capsule wall has specialized cells called
___________________________ (foot cell)
Podocytes form filtration slits –
Bowman’s capsule - drains into the Renal tubule
-
_______________________________________________________________________________________4_________
-
Renal tubule –
-
-By the time filtrate reaches the colllecting duct, its urine.
-Urine travels through collecting duct, through the
pyramids to the papillae, to the calyx
Urine Formation- 3 Processes
Filtration – Reabsorption – Secretion
Glomerular
Filtration
[nonselective]
*useful and waste are filtered
Summary of Urine Formation
The processes involved in urine formation are summarized below and illustrated above.
1. Glomerular filtration allows all diffusible materials to pass from the blood into the nephron .
2. Tubular reabsorption moves useful substances back into the blood while keeping waste products in the nephron to be eliminated in the urine.
3. Tubular secretion moves additional substances from the blood into the nephron for elimination .
Movement of hydrogen ions is one means by which the pH of body fluids is balanced.
Where does it
Happen?
What happens? What substances are involved?
Misc info
Glomerulus
[ball of yarn] and the of Bowman’s capsule
-blood plasma that does not leave through EFFERENT
ARTERIOLE moves from glom caps to the
B. capsule and becomes FILTRATE
-some solutes go with filtrate [water, salts ,
Electrolytes]
- some TOO BIG to cross [proteins, blood cells]
-180 L Filtrate/day
enters tubules
-vasoconstrict
EFFERENT arteriole…..what will happen to amount of filtrate?
Tubular
Reabsorption
[selective]
Where does it
Happen?
What happens? What substances are involved?
Renal Tubule TO
Peritubular capillaries
[offshoot of EFF Art]
-returns needed materials from tubule to the blood [peri caps]
- leaves waste in tubule
-solids, amino acids,
Na+, water , glucose
Misc info
- 99% is reabsorbed back into blood
-1% or 1.8 L becomes urine
4 Methods for Reabsorption:
1. diffusion (solids)
2. osmosis (liquids - H20)
3. Active Transport (Amino Acids, Na+)
4. Facilitated Diffusion (Glucose)
Tubular
Secretion
*opposite of reabsorption
Sites for reabsorption
PCT (microvilli)
Loop of Henle
(Desc. /Asc Limb)
DCT
Collecting Duct
%-age
70%
12%
17%
_____________
99% is reabsorbed.
This leaves 1% (1.8L) - excreted as urine.
Where does it
Happen?
What happens? What substances are involved?
Peritubular capillaries
TO Renal Tubule
-things not eliminated during filtration are transported during secretion [things that are still in blood]
-last effort to get rid of things
-H+ [bicarbonate ion for blood pH], K+, urea, uric acid, penicillin [UTIs]
Misc info
-Urea and uric acid are nitrogenous waste from liver- give urine yellow color
____________________________________________________________________________________________7___
IMPORTANT CHEMICALS IN THE URINARY SYSTEM
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus-
• The cells in these 2 locations are special
• Cells secrete an enzyme –
Renin stimulates a conversion of hormones from the liver and lungs.
• Angiotension II –
Stimulates Aldosterone [adrenal glands] and ADH [pit gland]
Aldosterone tells the DCT and Collecting Duct to
_______________________________.
• It follows that when Na+ is reabsorbed into the
blood, H20 will follow, increasing Blood volume,
and thus, blood pressure.
ADH works with aldosterone.
• ADH makes the cells of the collecting duct
and DCT more permeable to H20 for reabsorption.
• Water moves from tubules to capillaries,
resulting in increased blood volume and increased
blood pressure
_______________________________________________________________________________________8_________
URETERS, BLADDER and URETHRA
Ureters :
Urination:
Urinary Bladder :
Urethra :