quarter 4 - chapter 46 excretory system
advertisement

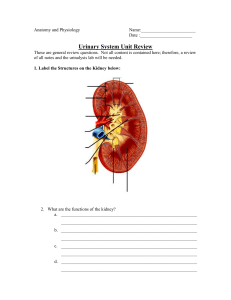
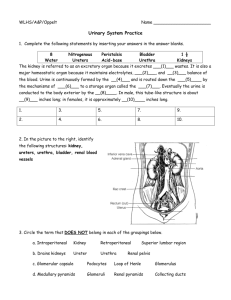
Independent Study – Quarter 4 Chapter 46: Osmoregulation and Disposal of Metabolic Wastes Answer the questions completely. Check out the figures, pictures, tables and diagrams as you go. This will be collected for points and graded for effort/completion and randomly checked for accuracy. 1. What are the 2 processes the body uses to maintain homeostasis of fluids in animals? Define both terms. 2. Describe urine. 3. Discuss the difference between elimination and excretion. 4. Why must waste be excreted from the body? 5. Explain how each of the following is excreted: a. Carbon dioxide b. Water c. Nitrogenous wastes 6. Describe and discuss the following in detail. a. Uric acid b. Urea c. Osmoconformer d. Osmoregulator e. Nephridial organs f. Nephridiopores 1 7. What kinds of organisms possess the following types of organs? a. Protonephridia b. Metanephridia c. Malpighian tubules d. Kidney 8. What is the job of the mammalian kidney? 9. Describe the roles of the following chemicals for kidneys. a. Rennin b. Erythropoietin c. 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3 10. What are the parts of the mammalian urinary system? 11. Describe the following for the kidney: a. Location, size b. Renal cortex c. Renal medulla d. Renal pyramids e. Renal papilla 2 f. Collecting ducts g. Urination h. Urethra 12. Outline the path of urine from the collecting ducts to the urinary bladder. 13. Describe how the bladder size can change. 14. Describe the structure of a nephron. What is it? Include a discussion of Bowman’s capsule, the renal tubule, glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule. 15. Discuss the 2 types of nephrons. 16. How is urine produced? Describe the following in detail. a. Filtration 3 b. Reabsorption i. How much filtrate is reabsorbed and how much is excreted as urine in 24 hours? c. Tubular transport maximum d. Tubular secretion 17. How does a salt gradient help to create concentrated urine? 18. What is the composition of urine? 19. What is urinalysis? What can it be used for? 20. What is the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)? 21. Describe how diabetes insipidus work? (or not work…) 22. What is the job of aldosterone? 4