Anatomy and Physiology II Renal/ Urinary Systems Study Guide
advertisement

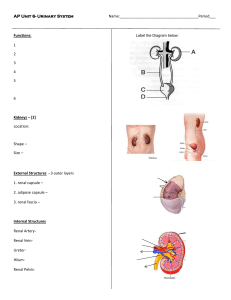
Anatomy and Physiology II Renal/ Urinary Systems Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. List the five functions of the renal and urinary systems In what space, are the kidneys located? What does the renal fascia do? What type of tissue is renal fascia composed of? What is the renal capsule and how does it differ from the renal fascia and adipose capsule? Be able to label a diagram of the kidney and describe in words; hilum, cortex, medulla, renal pyramids, renal column, renal papilla, minor and major calices, and renal pelvis What is a nephron and how many are in each kidney? Where in the kidney are nephrons located? What are the two types of nephrons in humans? Describe all structures associated with a nephron Where do afferent arterioles originate and where do they empty? What is called when the afferent arterioles divide many times? What surrounds the divisions of the aff. Arterioles? What happens to the diameter of afferent arterioles as they approach the efferent arteriole? Describe the path taken by the efferent arteriole: What tubule extends from Bowman’s capsule? Describe its shape What is the name of the loop that extends from the PCT and dips deep into the renal medulla? Describe in order all of the structures that blood and filtrate flow through before leaving the body: In what ways does the nephron form urine? What is the driving force of urine formation in glomerular filtration? Why does that driving force exist? What are the primary components of filtrate? What substances are not in filtrate? What is happening if substances from the previous study question are found in urine and filtrate? What percentage of filtrate is reabsorbed? What is the normal glomerular filtration rate in humans with adequate fluid volume and blood pressure? How does blood pressure affect glomerular filtration? What mechanisms are in place that ensure the rate of GFR? How does activation of the rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone feedback loop alter blood pressure? In what region of the nephron does the majority of reabsorption occur? What does the term threshold value refer to? PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. What happens if the threshold value is exceeded? What is the driving force of reabsorption? What hormone controls reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule? Which direction do substances move if they are being reabsorbed? a. Tubule to capillary or capillary to tubule Which direction do substances move if they are being secreted? What substances need to be secreted? Where does secretion occur in the nephron? What is the average volume of urine per day? What happens to the urinary output if a patient has an increased level of solutes in their urine? List all of the organs required for urine formation and elimination: What type of muscle is found in the ureters? What is the primary muscle found in the bladder? Is that muscle under voluntary or involuntary control? How much urine can be stored in the bladder? What is the name of the tube that extends from the bladder to the urinary meatus? What prevents urine from spilling out of the tube? What does ADH do to urine formation and how does it affect the volume of urine produced? What does aldosterone do to urine formation and how does it affect the volume of urine being produced? How does the nervous system regulate urine formation? What region of the brain senses the osmolarity of the urine and filtrate? What is dialysis? How is it performed? PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com