File - Mr. Williams
advertisement

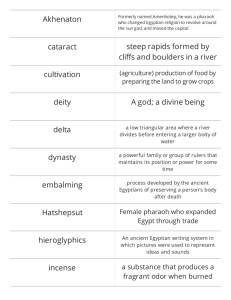
Part 3 - Exploring with Mr. Williams • Menes (review) • Khufu • Ramses II (a.k.a. Ramses the Great) • Hatshepsut • King Tutankhamun (already covered) • Cleopatra • Considered by many to be the first pharaoh • United Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt through war • Had a neat crown that combined the white and red crowns of the two kingdoms into one. • Supposedly reigned 62 years and was killed by a hippopotamus • Greeks called him Cheops, which is probably more well-known than Khufu. • Traditionally thought to be a very cruel king, though there is little evidence to support this. • Known because the Great Pyramid of Khufu was built during his reign. • Most well-known for banishing worship of all but the Sun god Aten. • After their death Tutankhamun and his successors restored the old gods. • Their names were removed from inscriptions, and their temples were torn down. • Has Nefertiti’s tomb been found? Time will tell. • Trained at a young age as a ruler and fighter • Made an army captain at age 10 • Well-known for the massive monuments he built such as the temples at Karnak and Luxor • Greatly increased the size of his kingdom • Considered by many to be the last great Egyptian pharaoh • First great woman in recorded history • Was married to the pharaoh Thutmose II, her half brother. He died young, leaving the throne to Thutmose III, a son by another woman. • Because Thutmose III was still very young, Hatshepsut took over power. • Because many people did not think women should rule, she dressed as a man, wore the pharaoh’s crown and royal ceremonial beard, and called herself king. • Ruled 20 years. • When she died, her stepson took back power and had her name stricken from all monuments she built. • 69-30 BC (ruled MUCH later than the other pharaohs we’ve studied) • Greek by birth • Highly educated, spoke 7 languages • Was 17 when her father died, and she and her brother were made co-rulers of Egypt • Had children with Julius Caesar and Mark Anthony. • According to legend, she committed suicide by poisoning herself with the venom of a deadly snake. • Horrible Histories Cleopatra Song https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a l5NxDmPdrs&index=6&list=PLwE2Nxu QmGw5taiW5lhLKPqi5eOg0gi0- • Valley where for 500 years the pharaohs and nobles of the New Kingdom were buried • 63 known tombs • Valley of the Kings https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =iIF7BActSZY • Period in Egyptian history that lasted about 500 years, from 2700 to 2200 BC. • Developed political system with pharaoh as both a king and a god. • First and some of largest pyramids built in this period. • Power struggles, crop failures, cost of building pyramids lead to its decline. • 2050-1750 BC • Drainage project creates more farmland • Trade developed with the Middle East and Crete • Corruption and rebellion common • Group called Hyksos invade using horse, chariots, and advanced weapons to conquer and rule Lower Egypt for 200 years. • 1550-1050 BC • Height of Egyptian power and glory • Hyksos defeated and empire greatly expanded. • Trade greatly increased • Conquered kingdoms and those wanting to maintain good relations make Egypt wealthy with gifts such as gold, precious, stones, and leopard skins. • Egyptian writing system, one of the first in the world. • More than 600 symbols, each representing one more sounds in the Egyptian language. • Could be written horizontally or vertically, right to left or left to write • Extremely difficult to read • Papyrus – long-lasting, paperlike material made from reeds • Cartouche – Oval name plate • Scholars couldn’t read hieroglyphics until the discovery of the Rosetta Stone • Huge stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics • Originally set up in a temple as a “thank you” to Ptolemy V, a Greek ruler of Egypt • Found in 1799 by a French soldier • French archaeologist Jean-Francois Champollion spent 20 years studying and deciphering the symbols • Same text in ancient Egyptian, in a later form of Egyptian, and in Greek • Currently most visited item in the British Museum • A cartouche is a rectangular plaque with rounded corners which contains hieroglyphics that represent a person’s name, usually a pharaoh. • They were used as nameplates on a sarcophagus, tomb, etc. to show who they belonged to.