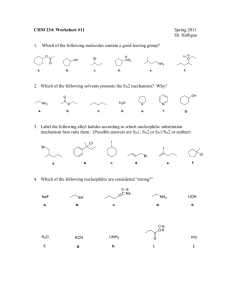
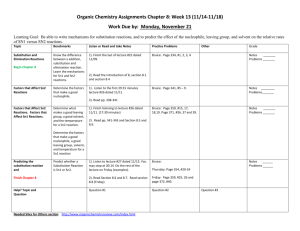
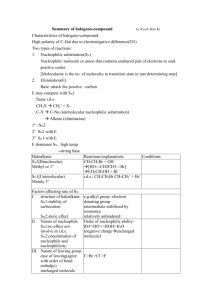
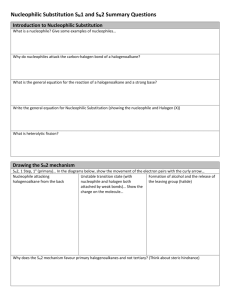
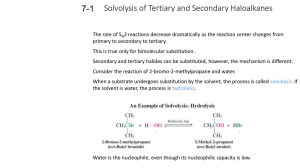
Reactions of Alkyl Halides
advertisement

Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic Substitution Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 2 3 Interesting Alkyl Halides 4 5 6 Reactions of Alkyl Halides 7 General Features of a Substitution Reaction Three components are necessary in any substitution reaction. 8 When a neutral nucleophile is used, the substitution product bears a positive charge. 9 10 11 Nucleophiles Basicity is a thermodynamic property Nucleophilicity is a kinetic property 12 • Steric hindrance decreases nucleophilicity but not basicity. 13 14 But what is the order of bond making and bond breaking? In theory, there are two possibilities. [1] Bond making and bond breaking occur at the same time. This is an example of an SN2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular) mechanism. 15 [2] Bond breaking occurs before bond making. This is an example of an SN1 (substitution nucleophilic unimolecular) mechanism. 16 SN2 Reaction CH3Br + OH– Rate = k[CH3Br][OH-] CH3OH + Br– a second-order reaction All SN2 reactions proceed with backside attack of the nucleophile, resulting in inversion of configuration at a stereogenic center. 18 19 20 21 The SN2 reaction is a key step in the laboratory synthesis of many important drugs. 22 23 24 25 26 • The rate of an SN1 reaction is affected by the type of alkyl halide involved. • This trend is exactly opposite to that observed in SN2 reactions. 27 28 29 The Hammond Postulate 30 31 32 • The strong nucleophile favors an SN2 mechanism. • The weak nucleophile favors an SN1 mechanism. 33 • A better leaving group increases the rate of both SN1 and SN2 reactions. 34 35 36 37 In addition to substitution, an alkyl halide can undergo an elimination reaction The E2 Reaction The Regioselectivity of the E2 Reaction The major product of an E2 reaction is the most stable alkene The greater the number of substituents, the more stable is the alkene (The Zaitsev Rule) Potential Energies of Pentene Isomers Consider the regioselectivity of the E2 reaction The alkene with the bulkiest groups on opposite sides of the double bond will be formed in greater yield, because it is the more stable alkene The E1 Reaction Elimination from Cyclic Compounds In an E2 reaction, groups to be eliminated must be trans to one another (anti-coplanar) Competition Between Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides can undergo SN2, SN1, E2 and E1 1) decide whether the reaction conditions favor SN2/E2 or SN1/E1 •SN2/E2 reactions are favored by a high concentration of nucleophile/strong base •SN1/E1 reactions are favored by a poor nucleophile/weak base 2) decide how much of the product will be the substitution product and how much of the product will be the elimination product Apakah mekanisme reaksi yang berkaitan dengan reaksi berikut, substitusi SN1 atau SN2? Jelaskan alasan Saudara 1.(CH3)3CBr + CH3OH (CH3)3COCH3 + HBr 2.CH3CH2I + NaCN CH3CH2CN + NaI H H c. + + HBr CH3OH OCH3 Br d. H H + Br CH3O-Na+ + NaBr OCH3