CHM 234: Worksheet #1
advertisement

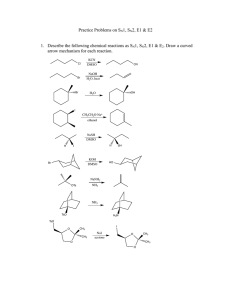
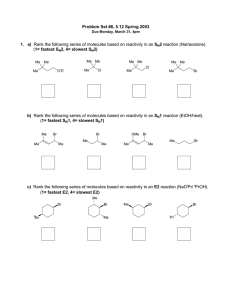
CHM 234: Worksheet #11 Spring 2011 Dr. Halligan 1. Which of the following molecules contain a good leaving group? 2. Which of the following solvents promote the SN2 mechanism? Why? 3. Label the following alkyl halides according to which nucleophilic substitution mechanism best suits them. (Possible answers are SN1, SN2 or SN1/SN2 or neither) 4. Which of the following nucleophiles are considered “strong?” 5. Which of the following solvents promote the SN1 mechanism? Why? 6. Rank the following alkyl halides in order of decreasing reactivity in an SN2 reaction (“1” is most reactive and “4” is least reactive). 7. Write a mechanism for the following SN2 reactions (a-e). 8. Which SN2 reaction in each of the following pairs will take place more rapidly? ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9. Classify the following carbocations in each set as 1°, 2° or 3° and then circle the most stable carbocation. 10. Rank the following alkyl halides in order of decreasing reactivity in an SN1 reaction (“1” is most reactive and “4” is least reactive). 11. Write a mechanism and give the products that will be obtained from the following reactions (a-c). 12. Give the substitution products obtained when each of the following compounds is added to a solution of sodium acetate in acetic acid. a. 2-chloro-2-methyl-3-hexene b. 3-bromo-1-methylcyclohexene 13. Propose a mechanism that leads to both the major and minor products for the solvolysis of 3,3-dimethyl-2-iodobutane in a solution of methanol. 14. Design a synthesis for the following targets from ethyne. Show the retrosynthetic analysis first; then write the synthesis. You will need to incorporate alkene, alkyne and substitution reactions.