Halogeno-compounds
advertisement
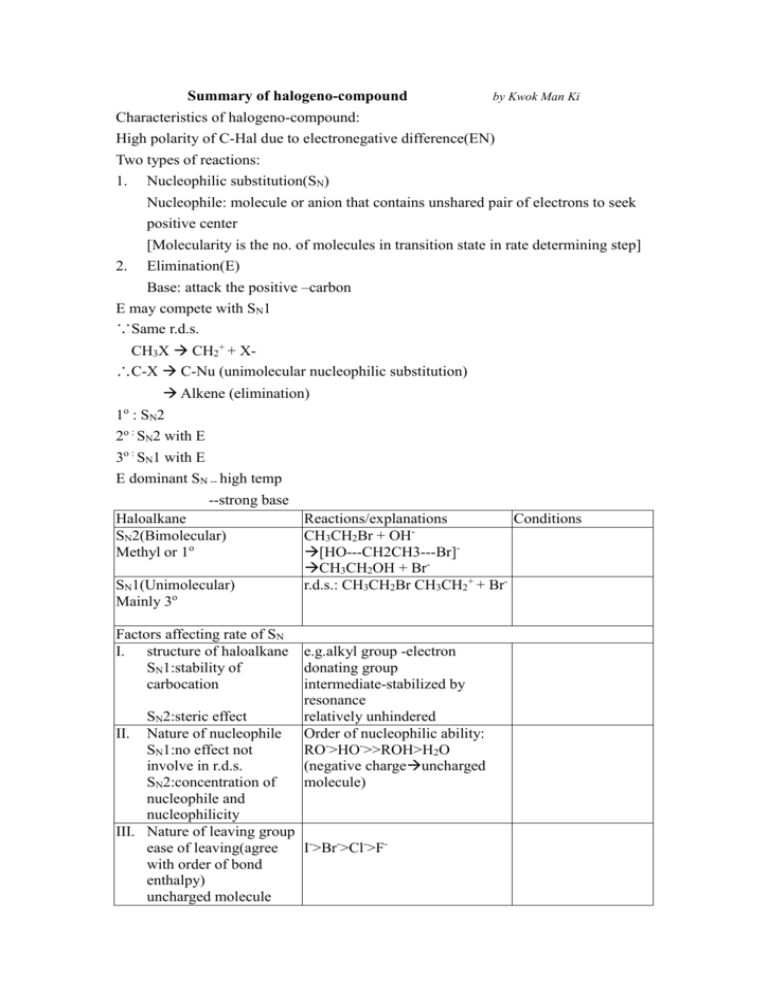
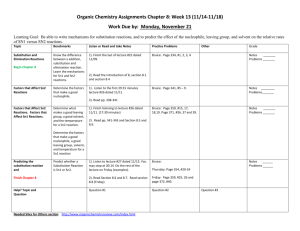
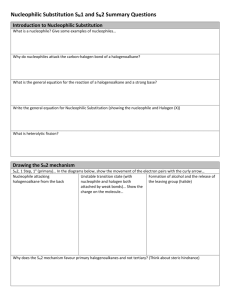
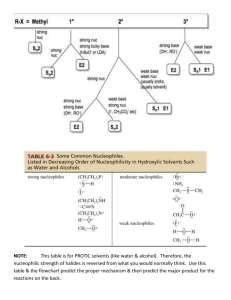
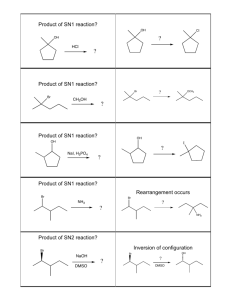
Summary of halogeno-compound by Kwok Man Ki Characteristics of halogeno-compound: High polarity of C-Hal due to electronegative difference(EN) Two types of reactions: 1. Nucleophilic substitution(SN) Nucleophile: molecule or anion that contains unshared pair of electrons to seek positive center [Molecularity is the no. of molecules in transition state in rate determining step] 2. Elimination(E) Base: attack the positive –carbon E may compete with SN1 ∵Same r.d.s. CH3X CH2+ + X∴C-X C-Nu (unimolecular nucleophilic substitution) Alkene (elimination) 1 : SN2 2o : SN2 with E 3o : SN1 with E E dominant SN -- high temp --strong base Haloalkane Reactions/explanations Conditions SN2(Bimolecular) CH3CH2Br + OH Methyl or 1o [HO---CH2CH3---Br]CH3CH2OH + BrSN1(Unimolecular) r.d.s.: CH3CH2Br CH3CH2+ + BrMainly 3o o Factors affecting rate of SN I. structure of haloalkane SN1:stability of carbocation e.g.alkyl group -electron donating group intermediate-stabilized by resonance relatively unhindered Order of nucleophilic ability: RO->HO->>ROH>H2O (negative chargeuncharged molecule) SN2:steric effect II. Nature of nucleophile SN1:no effect not involve in r.d.s. SN2:concentration of nucleophile and nucleophilicity III. Nature of leaving group ease of leaving(agree I->Br->Cl->Fwith order of bond enthalpy) uncharged molecule -better leaving group Protonation(alcohol in acid) Rate of reaction: Unreactivity of Halobenzene ∵C-X bond has multiple bond character ∴ no SN2 ∵Sp2 overlap C-X bond shorter and bond enthalpy larger ∵If SN1 loss of aromaticity Elimination Halide Dihalides (-2mole Br) Formation of bond C-C: ↑1 carbon atom C-O bond: alcohol ether C-N bond Conc.NH3 mixture of products may be formed ∵alkyl group bonded to N act as electron donating group→nucleophilic power↑ large excess of NH3 CN- as base(↑1 C) H2O>>OH->ORHX + R-OH+ R-X + H2O (neutral; good leaving group) SN1+SN2>SN1>SN2 e.g. Ar–CH2X Ar-COCl (Both O and Cl are electronegative to withdraw electrons form C, making C become more positive) H-C-C-Br -C=CBr-C-C-Br -C≡C- Alcoholic NaOH Excess KOH/C2H5OH with reflux R-C-Br + R-C-CN COOH KCN/alcohol;H+ ≠HCN ∵weak base→ poor nucleophile toxic gas R-X R-OH NaOH/reflux R-X R-O-R CH3CH2O-Na+/reflux (CH3CH2-OH + Na CH3CH2O- + Na+ + H2 Mixture of products CH3CH2-X + NH3 CH3CH2-NH2 (CH3CH2)2-NH (CH3CH2)3-N (CH3CH2)4-N+XNH3 + CH3CH2I CH3CH2-NH2 (monosubstituted) CH3CH2I + CN- LiAlH4/ether or CH3CH2CH2-NH2 2H2/Ni