Action
advertisement

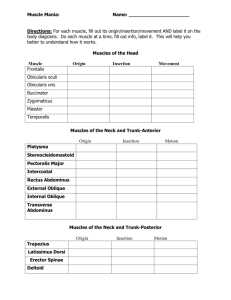
8.8 Major Skeletal Muscles What muscle names tell us Relative size Shape Location Action Number of attachments Direction of fibers Examples Zygomaticus – originates at the zygomatic bone Gluteus maximus – originates in the gluteal region and is a large muscle Tibialis anterior – originates on the anterior surface of the tibia Muscles of Facial Expression Epicranus Origin – occipital bone Insertion – skin and muscles around eye Action – raises eyebrow Orbicularis oculi Origin – maxillary and frontal bones Insertion – skin around eye Action – closes eye Orbicularis oris Origin – muscles near the mouth Insertion – skin of lips Action – closes and protrudes lips Buccinator Origin – outer surfaces of maxilla and mandible Insertion – orbicularis oris Action – compresses cheeks inward Zygomaticus Origin – zygomatic bone Insertion – orbicularis oris Action – raises corner of mouth Platysma Origin – fascia in upper chest Insertion – lower border of mandible Action – draws angle of mouth downward Muscles of Mastication Masseter Origin – lower border of zygomatic arch Insertion – lateral surface of mandible Action – closes jaw Temporalis Origin – temporal bone Insertion – coronoid process and lateral surface of mandible Action – closes jaw Muscles that move the head Sternocleidomastoid Origin – anterior surface of sternum and upper surface of clavicle Insertion – mastoid process of temporal bone Action – pulls head to one side, pulls head toward chest, or raises sternum Splenius capitis Origin – spinous processes of lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae Insertion – mastoid process of temporal bone Action – rotates head, bends head to one side, or brings head into an upright position. Semispinalis capitis Origin – processes of lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae Insertion – occipital bone Action – extends head, bends head to one side, or rotates head. Muscles that move the pectoral girdle Closely associated with those that move the arm. Many of these move the scapula up and down, back and forth. Muscles that move the pectoral girdle Trapezius Origin – occipital bone and spines of cervical and thoracic vertebrae Insertion – clavicle; spine and acromion process of scapula Action – rotate scapula and raises arm, raises scapula, pulls scapula medially or pulls scapula and shoulder downward. Rhomboideus major Origin – spines of upper thoracic vertebrae Insertion – medial border of scapula Action – raises and adducts scapula Levator scapula Origin – transverse process of cervical vertebrae Insertion – medial margin of scapula Action – elevates scapula Serratus anterior Origin – outer surface of upper ribs Insertion – ventral surface of scapula Action – pulls scapula anteriorly and downward Pectoralis minor Origin – sternal ends of upper ribs Insertion – coracoid process of scapula Action – pulls scapula anteriorly and downward or raises ribs Muscles that move the arm Arm is freely movable. Muscles are grouped by their primary action. Flexion – flexors Extension – extensors Abduction – abductors Rotation - rotators Flexors Coracobrachialis Pectoralis major Coracobrachialis Extensors Teres major Latissimus dorsi Abductors Supraspinatus Deltoid Rotators Subscapularis Infraspinatus Teres minor Muscles that move the forearm Most forearm movement is accomplished by muscles that connect the radius or ulna to the humerus or pectoral girdle. Again, we have flexors, extensors and rotators. Flexors Biceps brachii Brachialis Brachioradialis Extensor Triceps brachii Rotators Supinator Pronator teres Pronator quadratus Muscles that move the hand Flexors Anterior side Flexor carpi radialis Flexor carpi ulnaris Palmaris longus Flexor digitorum profundus Extensors Posterior side Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum Muscles of the abdominal wall External oblique Internal oblique Transversus abdominis Rectus abdominis Muscles of the pelvic outlet Pelvic diaphragm Levator ani Urogenital diaphragm Superficial transversus perinei Bulbospongiosus Ischiocavernosus Muscles that move the thigh Anterior group Psoas major Iliacus Posterior group Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Tensor fasciae latae Muscles that move the leg Flex the knee Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Sartorius Extend the knee Quadriceps femoris group, consisting of: Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Muscles that move the foot Dorsal flexors Tibialis anterior Fibularis Extensor digitorum Plantar flexors Gastrocnemius Soleus Flexor digitorum longus