Principle Skeletal Muscles 2 - Lancaster Central School District
advertisement

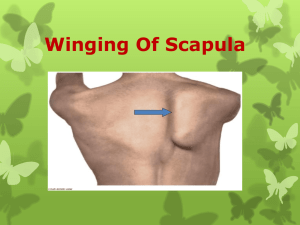
Principle Skeletal Muscles 2 Muscles that act on the abdominal wall, muscles used in breathing and muscles that move the pectoral girdle MUSCLES THAT ACT ON THE ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL The anterior abdominal wall is composed of skin, fascia and 4 pairs of muscles. Tendinous Intersections – bands of connective tissue that divides the rectus abdominis Linea Alba – tough fibrous band extending from xiphoid process to pubic symphysis Rectus Abdominis Origin – Pubis and Pubic Symphysis Insertion – Costal Cartilage and Xiphoid Process Action – Flexes vertebral column and compresses abdomen Linea Alba Tendinous Intersections External Oblique Origin – Lower 8 ribs Insertion – Crest of Ilium and Linea Alba Action – Compresses abdomen, flexes vertebral column. Singularly rotates vertebral column Internal Oblique Origin – Ilium, inguinal ligament Insertion – Costal Cartilage and linea alba Action - Compresses abdomen, flexes vertebral column. Singularly rotates vertebral column Transverse Abdominis Origin – Ilium, inguinal ligament, lumbar fascia, and costal cartilage Insertion – Xiphoid Process, linea alba and pubis Action – Compress Abdomen Muscles Used in Breathing These muscles alter the size of the thoracic cavity so that breathing can occur. Inhalation occurs when the thoracic cavity increases in size and exhalation occurs when the thoracic cavity decreases in size Diaphragm Origin – xiphoid process, costal cartilage and lumbar vertebrae Insertion – central tendon Action – increases the vertical dimension of the thoracic cavity resulting in inhalation. External and Internal Intercostals Origin – ribs Insertion – ribs Action: External – increases the anteroposterior and lateral dimensions of thoracic cage resulting in inhalation Internal – decreases the antroposterior and lateral dimensions resulting in forceful exhalation Muscles that Move the Pectoral Girdle These muscles are divided into anterior (pectoralis minor and serratus anterior) and posterior (trapezius, levator scapulae and rhomboid major) thoracic muscles based on their location. The main action of the muscles is to hold the scapula in place so that is can function as a stable origin for the muscles that move the humerus Pectoralis minor Origin – Ribs 3-5 Insertion – Scapula Action – depresses scapula, moves it laterally and forward Serratus Anterior Origin – Upper 8 or 9 ribs Insertion – Scapula Action – Moves scapula laterally and forward. AKA: “the boxer’s muscle” because it is important in horizontal arm movements like punching. Trapezius Origin – occipital bone, spines of C7 and thoracic vertebrae Insertion – clavicle and scapula Action – Elevates clavicle, moves scapula medially Levator Scapulae Origin – C1 – C5 Insertion – Scapula Action – elevates scapula Rhomboid Major Origin – Spines of T2-T5 Insertion – Scapula Action – Elevates scapula, moves it medially