The Muscular System
advertisement

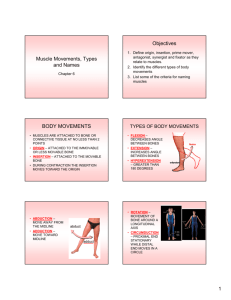
The Muscular System Chapter 10 Understanding Muscles • Pull never push • Attach to skeleton via tendons or muscles via aponeurosis • Attachment points – Origin: end attaches to a stationary bone; doesn’t move – Insertion: end attaches to a moving bone; moves • Contractions shorten muscles Functional Groups • Agonist (prime movers) – Prime responsibility for causing a movement • Antagonist – Oppose/reverse movement – Regulate agonist by adding resistance • Synergist – Assist prime mover – Add extra force or reduce undesirable movement • Fixators – Immobilize bone or muscle origin • Not mutually exclusive Naming Muscles • Location • Direction of fibers & – Bone or region associated w/ fasicles – E.g. brachii and femoris • Shape – E.g. deltoid and trapezius • Size – E.g. maximus, minimus, longus • Action – E.g. flexor , extensor, supinator – E.g. rectus, oblique, transversus • Number of origins – E.g. biceps and triceps • Location of attachment – Points of origin & insertion – E.g. sternocleidomastoid Fasicle Arrangement • Determines range of mov’t & power • Types – Parallel (fusiform) • Parallel to long axis – Pennate • Short & attach obliquely to an insertion tendon • Uni-, bi-, or multi – Convergent • Broad origin converges to an insertion – Circular • Concentric rings around external openings • Contractions close Lever Systems • A lever (bones) moves on a fulcrum (joints) when effort (muscle contraction) moves a load (bone and everything else) • Mechanical advantage (power lever) – – – – Effort farther from load then fulcrum Little effort needed Force gained for speed and stability E.g. car jack • Mechanical disadvantage (speed lever) – Effort nearer load then fulcrum – Force lost for speed and range – E.g. shovel Classes of Levers • First – Mechanical advantage or disadvantage • Second – Uncommon in body – Always mechanical advantage • Third – Most skeletal muscles – Always mechanical disadvantage Learning Muscles • Need to know – Names of major muscles – Basic functions/actions of muscles • Table 10.1 – Location • Studying – Learn names • Look for clues in names from existing knowledge • Draw and or act out • Identify on models or self