Muscular System Notes:
advertisement

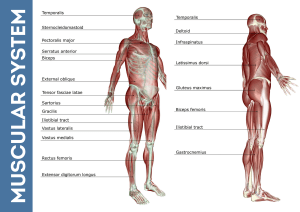
Muscular System Notes: Achilles tendon: Connects gastrocnemius to heel Aerobic Exercise: “with oxygen” does not deplete the muscle cells of oxygen, keeps heart and skeletal muscles working at steady pace Contract: “shorten” Muscles work by contracting and pulling, not pushing Endurance: How long you can maintain a given exercise or activity Flexibility: the range of motion possible around a joint Muscular System: all of the muscles and tendons in the body Skeletal Muscles: Attach to the skeleton via tendons; provide movement at joints Voluntary or conscious control Cells are long, straight, parallel fibers with striations or stripes contract to pull in one direction Smooth Muscles: found in many hollow organs in body (digestive tract, blood vessels, etc. involuntary control cells are shorter, more irregular in shape, not parallel contract in all directions to constrict or squeeze Strength: the maximum amount of work that a muscle can perform Tendon: Strong connective tissue fibers that attach muscles to bone Tissue: group of similar cells working together to perform a function or functions