Cells Core 40 review
advertisement

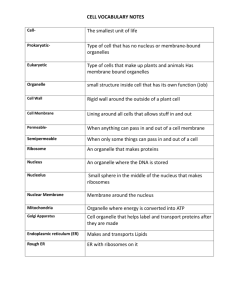
List in order the 6 steps of the scientific method. What is the purpose of an enzyme? At what temperature does the maximum activity of enzyme B occur? 1. Locate your bright ORANGE Core 40 Review Notes. Today’s Goal: Reinforce cellular biology including: -structure function of organelle -Cell Transport -Cell Division Elements Carbohydrates C,H,O C,H,O,N,S C,H,O,N,P Nucleotides C,H,O Ex-butter, oil Proteins growth & repair Ex-meat, cheese Nucleic Acids Ex-DNA,RNA Uses MonoEnergy saccharides Fatty Acids Energy & glycerol Amino Acids Structure, Ex-sugar,starch Lipids Building Blocks Genetic Information Examples of nucleic acids include A.sugars and starches B. DNA and RNA C. amino acids and fatty acids D. fats and proteins Which of the following is not normally a function of proteins in healthy cells? A. long-term energy storage B. functioning as enzymes C. a component of cell membranes Which of the following is an example of an organic chemical compound? A. B. C. D. carbon dioxide, CO2 sufur trioxide, SO3 sodium chloride, NaCl glucose, C6H12O6 Types of Cells Organelles and Functions Transportation Energy Photosynthesis Respiration Cell Division Cell Tissue – functioning group of cells Organ – functioning group of tissues Organ System – functioning group of organs Organism – functioning group of organ systems Homeostasis Steady State Self-adjusting mechanism that helps to maintain your internal environment Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell or Animal Cell? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell or Animal Cell? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Outside the Cell Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Inside the Cell Diffusion- movement of materials form a higher concentration to a lower concentration Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Osmosis- diffusion of water through a Membrane Passive transport is the movement of materials without energy Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion Active Transport requires energy Pumps, exocytosis, endocytosis Name the Organelle? Inside the Cell Enlarged Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Outside the Cell Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? Name the Organelle? ? Found in Plant Cells, Animal Cells or Both? What is it? DNA List the three parts of the Cell Theory. 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of life. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. What are the two basic types of cells? Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Which type of cell has a nucleus? Present your answers! Eukaryote This is the simpler of the two types of cells. Prokaryotes This type of cell has membranebound organelles. Eukaryotic ______________ is the thin, flexible barrier around all cells. Plasma membrane (Cell membrane) The plasma membrane is made up of two layers of ______________. Phospholipids What are the two parts of a phospholipid called? Head and a tail These molecules are located in the hydrophobic region of the membrane and strengthen the membrane. Cholesterol Scientists call the model they have developed to represent the structure of the plasma membrane the ______ ________ model. Fluid Mosaic What does it mean to be selectively permeable? To choose what goes in and what doesn’t T or F. All cells have cell membranes. Present your answers! True T or F. All cells have DNA. Present your answers! True T or F. All cells have cytoplasm. Present your answers! True T or F. All cells have a nucleus. Present your answers! False T or F. All cells have a cell wall. False – animal cells do not. What is the name of the membrane that surrounds the nucleus? Nuclear envelope What are the functions of the cytoskeleton? For cell support and movement The cytoskeleton is made up of what three components? Present your answers! Microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments What do ribosomes do for the cell? Present your answers! Make proteins Where can you find ribosomes in a cell? Present your answers! On rough ER, and in the cytoplasm (also in the nucleolus when they are being made What are the two types of Endoplasmic reticulum and what is the structural difference between the two types? Present your answers! Smooth and Rough – rough have ribosomes attached What does the ER do for the cell? Rough – modifies proteins Smooth – makes lipids and breaks down drugs and alcohol What does the Golgi apparatus do for the cell? Processes and packages proteins for export What is the function of a lysosome? To digest or break down food, old organelles, or other waste What type of molecules are inside lysosomes? (These molecules are what make the breaking down happen.) Enzymes What is the function of a central vacuole? A place for plants to store water, minerals, and waste; strengthens the cell and helps support the entire plant What do chloroplasts do for the cell? Convert energy from sunlight to chemical or food energy; perform photosynthesis Do animal cells have chloroplasts? Present your answers! No What is the function of the mitochondria? Present your answers! To make energy (the power plant of the cell) Animal, Plant, or Both: Cell Membrane Present your answers! Both Animal, Plant, or Both: Endoplasmic Reticulum Present your answers! Both Animal, Plant, or Both: Mitochondria Both Animal, Plant, or Both: Chloroplasts Present your answers! Plant Animal, Plant, or Both: Cell wall Present your answers! Plant Animal, Plant, or Both: Ribosomes Present your answers! Both Animal, Plant, or Both: Nucleus Present your answers! Both Animal, Plant, or Both: Golgi apparatus Both Types of Cells Organelles and Functions Transportation Energy Photosynthesis Respiration Cell Division 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Occurs in chloroplasts Two parts: Light reaction Calvin cycle (dark reaction) Cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to a form the cell can use. Energy is stored in an ATP molecule (adenosine triphosphate) . The process of breaking down food molecules to release energy Occurs in the mitochondria Two types: Aerobic – requires oxygen Anaerobic – occurs without oxygen C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Inseparable cycles The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis PMAT Cytokinesis Somatic Cells Reproductive Cells ASEXUAL Diploid cells produced by mitosis, binary fission Identical copy produced SEXUAL Gametes, haploid cells, produced by meiosis Gametes combine during fertilization to produce diploid cell First diploid cell known as a zygote Zygote grows into an embryo through mitosis Infinite possibilities Core 40 Test Practice Second Third Inning Visitor Home 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 First Total Home Outs Batter Up! Second Third Inning Visitor Home 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 First Total Home Outs 1.Place your Ecology Study Guide out for 10 pt. completion grade. 2.Cells Study guide due Friday. Today’s Goal: • Reinforce Cellular Chemistry and Structure. Per 6, 7 Biology Homework for week of April 23 - 27 Mon Tues Create Review PPT Weds Create Review PPT Th Digital PPT Presentations Genetics Study Guide Due Fri Last Current Event work day Biology Core 40 Test Tuesday May 8th