5.1 Introduction to carbonyl compounds
advertisement

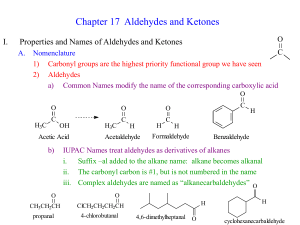
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS L.O.: Identify and name ketones and aldehydes CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - STRUCTURE Structure carbonyl groups consists of a carbon-oxygen double bond the bond is polar due to the difference in electronegativity Difference ALDEHYDES - at least one H attached to the carbonyl group H CH3 C=O H C=O H CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - STRUCTURE Structure carbonyl groups consists of a carbon-oxygen double bond the bond is polar due to the difference in electronegativity Difference ALDEHYDES - at least one H attached to the carbonyl group H CH3 C=O H C=O H KETONES - two carbons attached to the carbonyl group CH3 C2H5 C=O CH3 C=O CH3 R O C H or RCHO Aldehydes are named using the suffix –al. H O C or HCHO is methanal H O H Or C6H5CHO. Benzenecarbaldehyde Name this Aldehydes H O H C C H H H H O H C C C H H H H H O H C C C H H CH3 Ethanal Propanal 2-Methylpropanal Ketones are named using the suffix –one. H O H H C C C H H H Propanone (acetone) Name the following ketones H H O H H C C C C H H H H Butanone H H O H H H C C C C C H H H H H 3-Pentanone H H O H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H H 3-Hexanone H H O H H H H C C C C C C H H CH3 H H H 2-methyl-3-hexanone Solubility in water: Shorter chain aldehydes and ketones mix completely with water because of hydrogen bonds between the oxygen of the carbonyl group and water. As the length of the carbon increases, they become less soluble in water. Reactivity: