File
advertisement

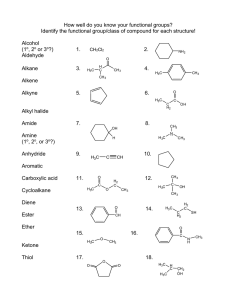
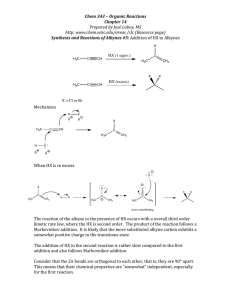
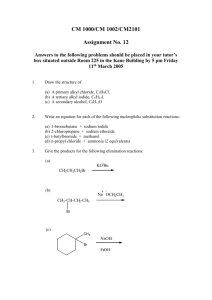
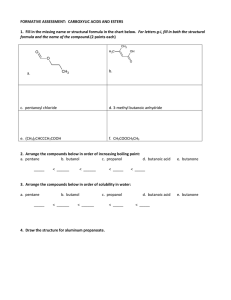
1. The structure of trans-1,2-Dimethylcyclobutane H 3C CH3 CH3 a. CH3 b. H3C CH3 c. CH3 d. H3C 2. Which of the following Newman projections represents 2,4-dimethylpentane? a. 4 b. 3 c. 2 d. 1 3. Which of the following contribute to the energy of conformations of butane? 1, torsional stain 2, steric strain 3, ring strain a. b. Only 1 Only 2 c. Only 1 and 2 d. 1, 2 and 3 4. Which one of the following structures represents a different compound from the other three? a. 4 b. 3 c. 2 d. 1 Cl H C 5. The IUPAC name for 3 a. 1-chloro-2,4-Diethyl[1.1.0]propane b. 5-chloro-2,4-Diethyl[1.1.1]pentane CH3 c. 1-chloro-1,3-Diethyl[1.1.0]propane d. 5-chloro-1,3-Diethyl[1.1.1]pentane CH3 6. The IUPAC name for a. 2-methyl-3-cycloheptanol b. 2-methyl-2-cyclohepten-1-ol OH c. 2-methyl-3-cycloheptenol d. 2-methyl-2-cycloheptenol 7. The important factor in the order of reactivity in SN2 is the spatial arrangement of the atoms or groups at or near the reacting site of a molecule which hinders or retards the reaction. This is called a. torsional effect c. steric effect b. ring effect d. all of the above 8. In an elimination reaction favors E1 over E2 if a. the substrate is a primary alkyl halide b. the substrate is a secondary alkyl halide c. the substrate is a tertiary alkyl halide d. the nucleophile is tert-butoxide 9. In a substitution reaction, when an alkyl halide is reacted with a R’O- nucleophile, the product would be a. an ether c. an alcohol b. a thiol d. an ester Cl H3C H H OCH3- + 10. The major product for the reaction above is H3C a. H H OH b. H3C O H H CH3 H3C c. H d. H3C O H H + H H