Biology 2015 Study Guide – Viruses, Bacteria and Infectious
advertisement

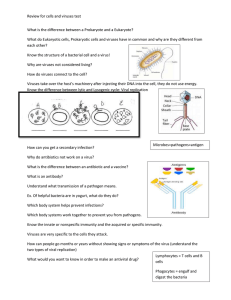
Biology 2015 Study Guide – Viruses, Bacteria and Infectious Disease Terms to know: bacteriophage capsid lytic cycle lysogenic cycle retrovirus binary fission conjugation obligate anaerobe obligate aerobe endospores prophage multi-drug resistant emerging disease heterotroph autotroph prokaryote zoonosis vector vaccine antibiotic infectious disease pathogen antigen antibody immunity white blood cell interferon histamines plasma cells memory B cell CDC WHO NIH Recall the following objectives given to you at the beginning of the study of this unit. Describe the key structures of: viruses, bacteria. Compare the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of viruses. Discuss the various ways in which viruses & bacteria are useful to humans. Identify how viruses and bacteria cause disease in humans, crops, and livestock. Describe how vaccines prevent viral infections. Explain how the overuse of antibiotics has led to the rise of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Write out complete answers to the following questions. 1. Draw and label a virus. 2. Are viruses living or not living? Explain your answer completely. 3. What is a retrovirus? Give an example. 4. Which is more damaging to living cells, the lytic or lysogenic phase of a virus? Biology 2015 5. Describe the lytic phase of a virus and its effects on the host cell. 6. Explain how a virus can spread in a bacterial population during the lysogenic phase of a virus. 7. How are bacteria different from viruses? Give a detailed explanation. 8. Compare and contrast the two domains of bacteria. 9. What is binary fission? 10. Of what benefit is conjugation to a bacterial population? 11. Identify several ways to keep one’s self safe from bacterial infection. a. b. c. 12. What is a pathogen? 13. Describe at least four ways in which pathogens/diseases are spread. 14. What do CDC, NIH, and WHO stand for? What is the general role of each? Biology 2015 Match the following terms with the correct description of nonspecific defenses. Terms: Cilia Fever inflammation histamine skin interferon mucous membrane Term Description 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Traps pathogens in the nose and throat Increases body temperature to slow growth of pathogens and activate some WBC’s Released by mast cells to increase flow of blood and fluids to an infected/affected area of the body. Sweep and push pathogens away from the lungs Barrier that stops pathogens from entering the body (largest organ of the body) Inhibits the making of viral proteins and helps block viral replication Body’s response to increase flow of white blood cells and fluid to an area. 22. What are antibodies? Describe their form and function. 23. What are antigens and what is their role in immunity? 24. Explain the difference between the body’s humoral immune response and cellular immune response. 25. How does the secondary response to a pathogen’s antigen differ from the primary response to that antigen? 26. Compare and contrast passive and active immunity. Biology 2015 27. What is an emerging disease? Explain and offer examples. 28. How do vaccines work? 29. Why is it so challenging to create vaccines against HIV or Ebola? Explain. 30. What are vectors? What is their connection between hosts and pathogens? 31. Describe three ways in which to prevent the spread of infectious disease. a. b. c.