Total Quality Management (TQM) Principles & Implementation
advertisement

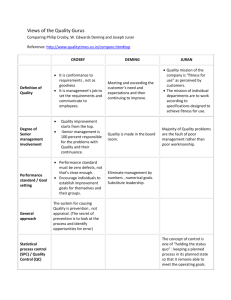
Total Quality Management(TQM) • The word “total” conveys the idea that all employees, throughout every function and level of organization, pursue quality. • The word “quality” suggests excellence in every aspect of the organization. • “Management” refers to the pursuit of quality results through a quality management process, including strategic, design, manufacturing, and finance processes. Principles of TQM • • • • The customer defines quality. Top management must provide the leadership for quality Quality is a strategic issue All functions of the company must focus on continuous quality improvement • Quality problems are solved through cooperation among employees and management • Use statistical quality control methods in problem solving • Training and education of all employees are the basis for CQI. Juran Trilogy Three aspects of quality managerial systems: • quality planning • quality control • quality improvement Elements of Quality Systems • • • • • • • • • Policy, planning, organization, and administration Product design assurance and specification development Control of purchased materials and component parts Production quality control and assurance Customer contact Corrective and preventive action Employee selection, training, and motivation Legal requirements - product liability and user safety Sampling and other statistical techniques Quality Policies • Mission statement outlines the specific need the firm’s product or service meets • Corporate policies (apply to everyone) • Departmental policies (not relevant to any other department worker) • Policies must be consistent with company’s strategy (buying from a low-cost bidder may be inconsistent with the strategy of high quality products) Deming’s 14 Points for Management • Create and publish to all employees a statement of the aims and purposes • Adopt the new philosophy • Understand the purpose of inspection • End the practice of awarding business on the basis of price tag alone • Improve constantly the system of production and service • Institute training • Teach and institute leadership Deming’s 14 Points (continued) • Drive out fear, create trust, create climate for innovation • Break down barriers between departments • Eliminate slogans , numerical quotas for production and other numerical goals • Remove barriers between employee and his/her supervisor • Encourage education and self-improvement • Take action to accomplish the transformation Deming’s View of Production as a System Suppliers Materials Equipment Test of materials Design and redesign Consumer research distribution A B C D Production, assembly, inspection Tests of processes, machines, methods, costs consumers Quality Cost Analysis • • • • Prevention costs Appraisal costs Internal failure costs External failure costs The major categories of cost as defined by the ASQ Employee Selection, Training, Motivation Motivation programs: • zero defects • quality control circles • participative quality control • employee involvement Legal Requirements • Product liability (examples: the Federal Meat Inspection Act of 1977, the Radiation Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968) • User safety (The Consumer Safety Commission - 1967)