Managing Quality 12 July 2001
advertisement

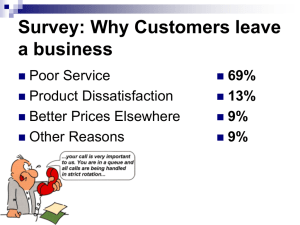
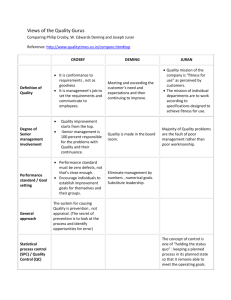
Managing Quality 12 July 2001 Introduction What: quality in operations management Where: Quality affects all goods and services Why: Customers demand quality What is Quality High quality products Low quality products What does quality mean to you? American Society for Quality “The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs” User-Based Definition “Quality lies in the eye of the beholder” Higher quality = better performance Higher quality = nicer features Manufacturing-Based Definition Quality = conforming to standards “Making it right the first time” Product-Based Definition Quality = a measurable variable Our Definition Quality: The ability of a product or service to meet customer needs Implications of Quality Company Reputation Product Liability Global Implications Global Implications National Quality Awards: US: Malcolm Baldridge National Quality Award Japan: Deming Prize Canada: National Quality Institute Canada Awards for Excellence Canada Award Winners 2000 Aeronautical and Technical Services British Columbia Transplant Society Delta Hotels Honeywell Water Controls Business Unit Quality and Strategy Differentiation Cost Leader Response Quality and Profitability Sales Gains •Improved Response •Higher Prices •Improved Reputation Improved Quality Increased Profits Reduced Costs •Increased Productivity •Lower Rework, Scrap •Lower Warranty Costs Costs of Quality Prevention Costs Appraisal Costs Internal Failure External Costs International Standards ISO 9000 Establish quality management procedures Documented processes Work Instructions Record Keeping Does NOT tell you how to make a product! Total Quality Management TQM – Total Quality Management Quality emphasis throughout an organization From suppliers through to customers W. Edwards Deming Deming’s 14 Points Create consistency of purpose Lead to promote change Build quality into the product, stop depending on inspections to catch problems Build long-term relationships based on performance instead of awarding business on the basis of price Continuously improve product, quality and service Start training Deming’s 14 Points Emphasize leadership Drive out fear Break down barriers between departments Stop haranguing workers Support, help and improve Remove barriers to pride in work Institute a vigorous program of education and self-improvement Put everybody in the company to work on transformation TQM Concepts Continuous Improvement Employee Empowerment Benchmarking Just-In-Time Taguchi Knowledge of Tools Continuous Improvement Act Plan Check Do Continuous Improvement Kaizen Zero Defects Six Sigma Employee Empowerment Involve employees in every step of production High involvement by those who understand the shortcomings of the system Quality circle Benchmarking Pick a standard or target to work towards Compare your performance Best practices in the industry Just-In-Time Produce or deliver goods just when they are needed Low inventory on hand Keeps evidence of errors fresh Taguchi Concepts Quality robustness Quality Loss Function Target-oriented Quality TQM Tools Check Sheet Scatter Diagram Cause and effect diagram (fishbone) Pareto Chart – 80-20 Rule Flow Charts Histogram Statistical Process Control Inspection Attribute Inspection Variable Inspection Inspection At supplier’s plant Upon receipt of goods from supplier Before costly processes During production When production complete Before delivery At point of customer contact Source Inspection Employees self-check their work Poka-yoke Statistical Process Control Apply statistical techniques to ensure processes meet standards Natural variations Assignable variations Goal: signal when assignable causes of a variation are present Statistics Mean Standard deviation Natural variation Assignable variation Control Charts X Bar Chart R Chart In Control vs Out Of Control In control and producing within control limits In control, but not producing within control limits Out of control Central Limit Theorem Mean Standard Deviation 95.5% 99.73% Control Limits Using Control Charts Mean changing – Range changing