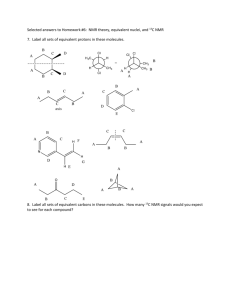
Modern C-13 NMR Spectroscopy
advertisement

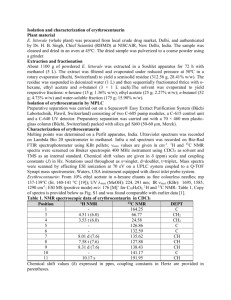
Advanced NMR Topics Second Order Effects in NMR • Splitting does not follow N+1; cannot be solved graphically – Different intensities – Additional peaks – Cannot directly measure coupling constants Causes of Second Order Spectra • Strong Coupling • Virtual Coupling • Magnetic nonequivalence Strong Coupling • Compare coupling constant (J) to difference in shift (Dn) • If Dn < 5J, then second order • Simplified by higher field instrument • 60MHz: Dn=0.3ppm(60Hz/ppm) = 18Hz; J= 18 Hz • 360MHz:Dn=0.3ppm(360Hz/ppm) = 108Hz; J= 18 Hz Pople Coupling Nomenclature • Spin system named by how close protons are in shift: A, M, X • AX2 system: one proton coupled to two protons with distant chemical shift (first order) • AB2 system: one proton coupled to two protons with similar shift (second order) • AMX3: one proton coupled to one proton coupled to three protons, all distant chemical shift (first order) First and Second order systems • http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/reich/nmr/05hmr-07-pople.htm • http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/reich/chem605 /index.htm Virtual Coupling Magnetic Equivalence • Chemical equivalence • Magnetic equivalence • AA’BB’ system: disubstituted benzene • Deceptively simple spectra Modern C-13 NMR Spectroscopy C-13 Sensitivity • Only 1% natural abundance • Split by protons • 13C/1H J = 125 Hz for sp3 carbon • Solution to problem: Broadband Decoupling – No splitting observed – Increases signal DEPT NMR • Distorsionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer • Transfer signal from protons to carbon 2D NMR • 2 basic experiments – COSY and HETCOR • COSY – H-H Correlation spectroscopy – 1H spectra on x and y axes • HETCOR – Heteronuclear correlation spectroscopy – 13C on one axis, 1H on the other (same sample) • There are many more 2D experiments – these are two of the most common Reading a COSY spectrum • X-axis = 1H spectrum • Y-axis = 1H spectrum • Diagonal = reference points (mirror plane: C=D) • Off-diagonal peaks = coupled protons Isopentyl acetate A = 1-2 coupling B= C= How to read a HETCOR spectrum • X-axis = 13C spectrum • Y-axis = 1H spectrum • No diagonal (no mirror plane) • Peaks indicate a 13C and the 1H’s directly attached to it. Isopentyl acetate In the C-13 spectrum, which carbon signal is furthest upfield? From induction, we might think that it is carbon 1, but… 5 6 1 • Very useful for – Finding overlapping proton signals – Identifying diasteriotopic carbon and protons atoms 3 3 4 2 Interpret all NMR spectra for 6-chlorohexanol (don’t need to calculate coupling constants): 1 2 4 3 6 5 7 Note: These NMR spectra were obtained in a solvent in which acidic protons are visible, and coupling to these protons is observed. 1H NMR 600 MHz 1 2 4 3 13C 6 5 7 NMR 150.9 MHz DEPT-90 DEPT-135 normal COSY 600 MHz 1 2 4 3 6 5 7 HETCOR 600 MHz 1 2 4 3 6 5 7 Ribavirin • Anti-viral • Used to treat hepatitis C • Guanosine analog— inhibitor or viral RNA synthesis Riboflavin DEPT DEPT 135 O N H HO H N O H 160 X : parts per Million : 13C 160.0 150.0 140.0 140 140.0 H N H HO 150.0 H H H 160.0 N H 130.0 130.0 OH 120.0 120 120.0 110.0 ppm 110.0 100.0 90.0 100.0 90.0 100 80.0 70.0 80.0 70.0 80 60.0 60 60.0 10.0 g f e d i h k j l 6.0 5.9 5.8 5.7 5.6 5.5 5.4 5.3 5.2 5.1 5.0 4.9 4.8 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 0 Y : parts per Million : 1H (Millions) Ribavirin COSY l k j i h g f e d 6.0 5.9 5.8 5.7 5.6 X : parts per Million : 1H 5.5 5.4 5.3 5.2 5.1 5.0 4.9 4.8 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 0 (Millions) 10.0 20.0 40.0 A B C D G E F H 0 (Thousands) Ribavirin HETCOR 4.0 l k j i h 5.0 g 6.0 f e d 7.0 g 8.0 b a 9.0 Y : parts per Million : 1H c 160.0 150.0 X : parts per Million : 13C 140.0 130.0 120.0 110.0 100.0 90.0 80.0 70.0 60.0 50.0 0 2.0 (Millions) 4.0 6.0 8.0