Macromolecules Notes - Liberty Union High School District

Macromolecules in Biology
(also known as biomolecules)
Chapter 2
Biomolecules Vocabulary
• Atom : smallest unit of matter (not alive)
– Most biomolecules are made of these atoms:
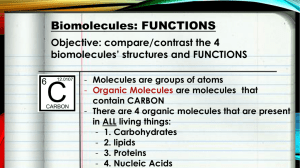
• Carbon (C)
• Hydrogen (H)
• Oxygen (O)
• Nitrogen (N)
• Phosphorus (P)
• Molecule : group of atoms bonded together
Examples: Water (H
2
O) and Salt (NaCl) are common molecules
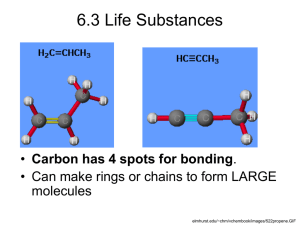
• Organic compounds : these are molecules that contain carbon (C)
– biomolecules are organic compounds
Sugar (carbohydrates)
Fat (lipids)
Amino acid (proteins)
• Monomer : simple molecules that link up to form a bigger compound (polymer)
(It is kind of like one link in a chain.)
• Polymer : molecules of many repeating units
3 monomers
Polymer
• Macromolecules : large polymers
• Biomolecules : organic molecules needed for life
– Proteins
– Nucleic Acids
(DNA and RNA)
– Carbohydrates
(sugars)
– Lipids (Fats)
Pair Share
• Which molecule is an organic compound?
– H
2
O
– NaCl
– C
6
H
12
O
2
– O
2
• How can you tell?
• Function : Used by all cells for energy and used by plants for structure.
• Structure : Includes all sugars, from simple sugars to complex polymer sugars.
• Energy is stored in the bonds between carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Carbohydrates
Types of Carbohydrates
• 1. Monosaccharides : One ring sugar (simple sugar)
– Ex : Glucose , fructose
• 2. Disaccharides : Two ring sugars
– Sucrose (table sugar)= glucose + fructose
– Maltose (beer sugar) = glucose + glucose
Carbohydrates
• 3. Polysaccharides : Many Ring sugars
– Starch : stores energy in plants.
– Glycogen : stores energy in animals.
– Cellulose : gives plant structural support.
A few examples of polysaccharides:
Starch – found in the potato
Glycogen – found in human muscles & in the liver.
Cellulose – another form of plant polysaccharide. Humans cannot digest it!
Cellulose = dietary fiber. Helps “scrub” out your digestive tract.
Pair Share
• What type of carbohydrate is the single-ring sugar called glucose:
– Monosaccharide?
– Disaccharide?
– Polysaccharide?
Lipids
Structure :
• Glycerol + 3 fatty acid molecules bonded together
•Large molecule
(not a polymer)
Functions :
– Part of cell membrane
(phospholipid)
– energy storage
– to cushion organs
•A fatty acid is lots of carbons bonded to hydrogens.
– insulation
Lipid Structure
Glycerol
Fatty Acid
This lipid has 3 glycerols and their fatty acids bonded together
A few examples of dietary fats:
(don’t copy this slide)
Unsaturated fats are found in many plant products, such as olive and canola oils, nuts, avocadoes, and also found in fish.
Saturated fats should be eaten in moderation, since they can lead to cholesterol build-up and heart disease.
Pair Share
• What is the most important function of a lipid?
Proteins
• Structure: A chain of amino acids
– also called polypeptides.
– different proteins have different sequences and amounts of amino acids
• Functions:
– Creates skin, muscle, hair, teeth, bone & other body structures
– Help transport materials from cell to cell
– Allows cells to signal each other
– Used in immune system defense
– Enzymes
Protein structure is based on the sequence of amino acids.
Pair Share
• Why is a protein an example of a macromolecule?
Nucleic Acids
• Nucleic Acids – DNA , RNA
– Structure – polymer is made up of nucleotide monomers
• Nucleotide
– Function
• Makes up the genetic code; provides instructions for making proteins.
DNA Polymer
Pair Share
• Why are DNA and RNA examples of macromolecules?
Pair Share
• In your own words, define macromolecule.
Copy this dichotomous key to quickly identify biomolecules.
Does it have a ring structure in its main chain?
Biomolecule Crash
Course Video
(14 min.)
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8WJ2
KENlK0