Life Substances: Biomolecules, Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins
advertisement
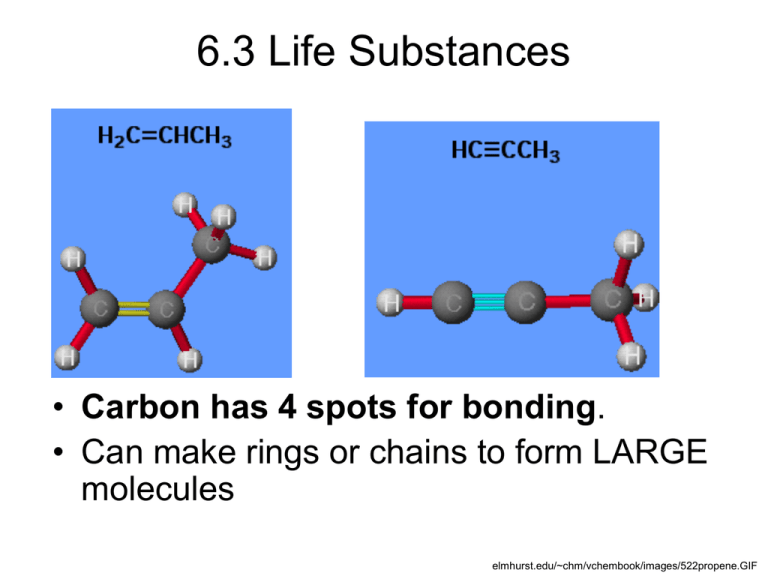
6.3 Life Substances • Carbon has 4 spots for bonding. • Can make rings or chains to form LARGE molecules elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/images/522propene.GIF 6.3 - Metabolism • Cell metabolism is the process (or really the sum of many ongoing individual processes) by which living cells process nutrient molecules and maintain a living state. • metabolism has two distinct divisions: – anabolism, in which a cell uses energy and reducing power to construct complex molecules and perform other life functions such a creating cellular structure; and – catabolism, in which a cell breaks down complex molecules to yield energy and reducing power. 6.3 Life Substances • Biomolecule – a large organic compound – 10-1000s of C atoms. • Polymer – a lg. molecule formed from several sm. molecules bonding together. Carbohydrates Main Function- Energy • Contain __, __, & __ • Polymer of single sugars • Monosaccharidesmall sugar – Glucose • Disaccharide – 2 sugars – Sucrose Carbohydrates – Polysaccharide - Examples Used by plants to store E Add strength to plant’s cell walls “Dietary Fiber” Used by animals to store E in muscle and liver Lipids • Functions – Energy storage – Forming the membranes around our cells. – Hormones and vitamins • Lots of ___ and ___, some ___ • Examples– Fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Lipids • Made up of fatty acids and ______ FATS OILS biology.clc.uc.edu/Courses/bio104/lipids.htm Proteins • The most important! • Contain ___, ___, ___, ____, ____ • Functions – Provide structure for tissues – Carry out cell metabolism (a.k.a everything) • Polymer of amino acids(aa) – Peptide bonds link each aa student.ccbcmd.edu/.../images/peptidebond.jpg Proteins • Enzymes- changes the rate of a chemical rxn. – Lock and key Nucleic Acids Functions – Stores cellular info in code. – DNA, RNA • Polymer of nucleotides 6.3 Life Substances 6.3 Life Substances • Source http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/BIOL115/Wyatt/