Biomolecule Power Point For Class Notes
advertisement
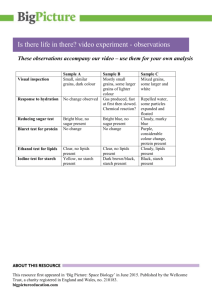
Section 2.3 Biomolecules What are the four types of biomolecules? Today you will: • Learn about each type of biomolecule • Learn how to test for the presence of each biomolecule in different food substances. Questions to discuss • In this lab you will put different food sources in a test tube to test for the presence of various macromolecules. Why will one of your test tubes be filled with distilled water? • What is the dependent variable? What is the independent variable? Biomolecules • Molecules are either inorganic compounds or organic compounds – Organic-has carbon – Inorganic-no carbon • Why is carbon so special? – It can form 4 bonds with other atoms. It loves to COVALENTLY BOND! – It can form single, double, and triple bonds. Biomolecules • There are 4 types of biomolecules in our bodies – – – – Carbohydrates Lipids (fats) Proteins Nucleic acid (DNA) • These are large molecules (polymer) that are made up of smaller building blocks (monomers) • Polymers are made of monomers. • http://www.phschool.com/scie nce/biology_place/biocoach/bi oprop/monomers.html Proteins • Elements: C, H, O, N, or S (sulfur) • Structure: look for N or S • What do they do-THEY DO A LOT! – – – – – Hemoglobin in your blood that carries oxygen Muscles, tendons, hair Defend body from microorganisms Control chemical reactions-enzymes Carry out almost all of the body’s everyday functions • Building block-amino acids Testing for proteins • You will use a biuret reagent • It will turn a blue violet color in the presence of a protein. • You will add each substance to a test tube and then add a few drops of biuret reagent. Carbohydrates • Elements-C, H, O • Function: Main source of energy, gives plants tough structure • Examples: sugars and starches, glycogen, sucrose, glucose, cellulose (END IN ose) • Shape-rings connected • Building Blockmonosaccharide or simple sugars (glucose) Different types of carbohydrates • Based on size – Monosaccharide-one sugar • MONO MEANS ONE – Disaccharide-two sugars • DI MEANS TWO – Polysaccharide-many sugars (2 OR MORE) • Cellulose-makes plants have a rigid structure • Glycogen-animal starch Two carbohydrate tests-starch and simple sugars • Starch – Iodine will turn black or purple in the presence of starch • Benedict’s solution – Add substances to tube with benedict’s solution – Heat for 3 to 5 minutes to look for color change – The redder the more simple sugar (glucose) present – Will form a percipitate • Not a polymer Lipids (Fats) – Why? Does not have the same unit repeating over and over • Elements-C, H, O • Has the most energy but we can’t consume tons of fat; part of membranes; insulation • Structure-long chain of carbons attached • Examples: cholesterol, wax, steroids, oils • Building Block-fatty acids and glycerol Saturated vs. Unsaturated • Saturated-bad for you; causes cholesterol problems, clogged arteries; solid at room temperature; lard • Unsaturated-liquid at room temperature; not as bad for you; olive oil, canola oil, peanut oil • Trans fat-type of unsaturated; causes coronary heart disease 2 ways to test for lipids • Brown paper bag – Substance will leave an oil spot if present • Sudan 4 test – Substance will turn red Nucleic Acids • Tell your cells how to function • Contains the genetic information • DNA (deoxyribose sugar) and RNA (ribose sugar) • Elements: C, H, O, N, P • We talk about these a TON second semester! So you only need to know these points.