File - Gleason Chemistry
advertisement

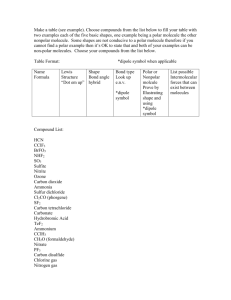
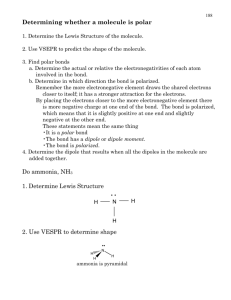
Ch. 10 Homework Questions 1. Discuss the basic features of the VSEPR model in how it predicts molecule geometry. 2. How does the magnitude of repulsion compare for the following lone pair-lone pair , lone pair bonding pair , bonding pair-bonding pair? 3. Predict the geometries of the following species using the VSEPR method: (a) PCl3 (b) CHCl3 (c) SiH4 (d) TeCl4 (e) CS2 (f) OF2 (g) N2 (h) NO2- 4. Classify each of the following bonds as either covalent, polar covalent, or ionic based on the electronegativity difference of the atoms. a) ClF3 b) FeCl3 c) NH3 d) CuF2 e) Br2 5. What is the relationship between the dipole moment and the bond moment? How is it possible for a molecule to have bond moments and yet be non-polar? 6. List the following molecules in order of increasing dipole moment: H2O, CBr4, H2S, HF, NH3, CO2. (Adapted from Chemistry by Chang) Attach Scratch paper as needed. Ch. 10 Homework Questions 7. Draw the dipole moments (the dashed arrow) found each bond in the following molecules 8. Based on the symmetry of the dipole moments above, classify each either polar or nonpolar. 9. How do polar substances interact with other polar substances (versus non-polar & polar)? 10.Which of the following molecules has a higher dipole moment? 11. How many sigma () and pi ( bonds are in the molecule below? (Adapted from Chemistry by Chang) Attach Scratch paper as needed. Ch. 10 Homework Questions 12. What is the hybridization of atomic orbitals? 13. Explain the details of bonding in methane (CH4) and how it illustrates hybridization. 14.Indicate the type of hybrid orbitals used by the central atom in the following compounds: a) CH4 b) PBr5 c) SF6 d) BCl3 15. What is molecular orbital theory? How does it differ from valence bond theory? (Adapted from Chemistry by Chang) Attach Scratch paper as needed.