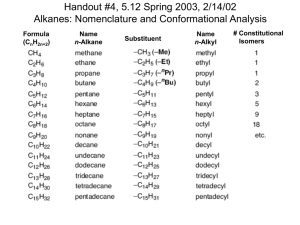
Chem 125 Lecture 10 9/26/07 Preliminary

Chemistry 125: Lecture 33
Conformational Energy and
Molecular Mechanics
Understanding conformational relationships makes it easy to draw idealized chair structures for cyclohexane and to visualize axial-equatorial interconversion. After quantitative consideration of the conformational energies of ethane, propane, and butane, cyclohexane is used to illustrate the utility of molecular mechanics as an alternative to quantum mechanics for estimating such energies. To give useful accuracy this empirical scheme requires thousands of arbitrary parameters. Unlike quantum mechanics, it assigns strain to specific sources such as bond stretching, bending, and twisting, and van der Waals repulsion or attraction.
Synchronize when the speaker finishes saying
“…in more detail than people wanted to hear about.”
Synchrony can be adjusted by using the pause(||) and run(>) controls.
For copyright notice see final page of this file
Ernst Mohr Illustrations (1918) confirm Sachse’s 1890 insight.
Ernst Mohr Illustrations (1918) flagpole bowsprit
“chair”
Red bonds rotate in & up.
“boat”
Blue bonds rotate in & down.
“ring flip” by 60° counter-rotation of two parallel bonds inverted chair
What o’clock?
Ernst Mohr Illustrations (1918)
?
?
?
?
Drawing chair cyclohexane rings: opposite C-C bonds parallel axial bonds parallel to 3-fold axis equatorial bonds parallel ( anti ) to next-adjacent C-C bonds
For such problems D.H.R. Barton
Invents Conformational Analysis
(1950)
Intermediates in steroid hormone synthesis
“up” ; “down”
(for molecule in conventional orientation, old-fashioned configuration notation, like cis / trans )
Barton redraws
Ring A
C
D
A B
Baeyer observed only one c-Hexyl-COOH, but in these epimers, and OH groups have different reactivity!
(configurationally diastereotopic)
For such problems D.H.R. Barton
Invents Conformational Analysis
(1950)
ERRORS?
“up” ; “down”
(for molecule in conventional orientation, old-fashioned configuration notation, like cis / trans )
Ring Flip?
)
(e) “equatorial”
(p) “polar” (now axial )
3-fold axis
Cf . ~1950 Stereochemistry:
Bijvoet, Newman, CIP,
(Molecular Mechanics)
(Nobel Prize 1969 for “development of the concept of conformation and its application in chemistry”)
Ernst Mohr Illustrations (1918) gauche OK within second ring of decalin, but not anti .
anti
N.B.
During ring flip equatorials become axials and vice versa .
gauche fused chairs in "decalin"
(decahydronaphthalene)
Try with models if you’re skeptical.
Ring flip impossible for trans decalin!
Mol4D
(CMBI Radboud University, Nijmegen, NL)
Conformational Jmol Animations
Click for INDEX or go to http://cheminf.cmbi.ru.nl/wetche/organic/index.html
(see Wiki to install Jmol)
Mol4D
(CMBI Radboud University, Nijmegen, NL)
Click Points
Ethane Click to Animate or go to http://cheminf.cmbi.ru.nl/wetche/organic/nalkanesconf/ethane/jmindex.html
Staggered
Eclipsed barrier ~5.2 kJ/mol 0.239 = 1.24 kcal/mol
Should be ~2.9 kcal/mol. Caveat emptor!
Step Keys
Mol4D
(CMBI Radboud University, Nijmegen, NL)
Propane Click to Animate or go to http://cheminf.cmbi.ru.nl/wetche/organic/nalkanesconf/propane/jmproprot.html
Eclipsed
3.3 kcal/mol
Staggered
Mol4D
(CMBI Radboud University, Nijmegen, NL)
Butane
(central bond) Click to Animate or go to http://cheminf.cmbi.ru.nl/wetche/organic/nalkanesconf/butane/jmindex.html
10 13
Anti
10
-3/4
Gauche
3.4
10
+
10.5
/sec eclipsed
3.4 kcal/mol
(tells how fast)
OOPS!
fully eclipsed
~ 4.4 kcal/mol?
(experimentally irrelevant)
Gauche
-
Anti Gauche
+
0.9 kcal/mol
(tells how much)
Gauche / Anti = 10 -3/4 0.9
= 10 -0.68
= 1 / 4.7
Gauche / Anti = 2 10 -3/4 0.9
= 2 10 -0.68
= 1 / 2.4
Mol4D
(CMBI Radboud University, Nijmegen, NL)
Ring Flip of c -Hexane Click to Animate or go to http://cheminf.cmbi.ru.nl/wetche/organic/cyclohexane/jm/chxjmol.html
Barrier ( Half-Chair )
~ 11 kcal/mol
Chair conformer
Flexible or
Twist-Boat conformer
~5.5 kcal/mol
Mol4D
(CMBI Radboud University, Nijmegen, NL)
Flexible c -Hexane Click to Animate or go to http://cheminf.cmbi.ru.nl/wetche/organic/cyclohexane/jm/twist_boat.html
Barrier ( Boat )
~ 1 kcal/mol
Flexible or
Twist-Boat Form
Shape,
“Strain Energy”
&
Molecular Mechanics
“Hooke’s Law” for Strain Energy
Conformational Energy of Ethane
3 kcal/mol
0°
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
120°
H H
Torsional Angle
H
240°
H H
H H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
360°
H H
H
H
Conformational Energy of Butane
4.4 kcal/mol
4.4 kcal/mol
3.4 kcal/mol
0°
CH CH
3
H
H
0.9 kcal/mol
H
H
H
3
CH
3
H
0.9 kcal/mol
120°
CH
3
H
Torsional Angle
240°
CH
3
H
3
H
H
CH
3
H H
CH
H 3
H
H
3
CH
3
CH
3
H
H H
H
360°
CH
3
H
H
Molecular Mechanics (1946)
“Molecular Mechanics” programs calculate (and can minimize) strain assuming that molecules can be treated as mechanical entities.
To achieve useful precision they require a very large set of empirical force constants adjusted arbitrarily to make energies match experiment
(or reliable quantum calculations).
“MM2” Parameters
66 different atoms types (including 14 different types of carbon)
138 different bond stretches
(41 alkane carbon-X bonds)
“MM2” Parameters
66 different atoms types (including 14 different types of carbon)
624 different bond bendings
(41 alkane-alkane-X angles)
“MM2” Parameters
66 different atoms types (including 14 different types of carbon)
0.5
Overall Butane 180° is low
“because of” reduced anti
1494 tweaked by van der Waals different bond twistings torsional energy
(37 alkane-alkane alkane-X twists)
Sum:
1-1-1-1 Torsional Contribution to Butane
-0.5
After simplification “MM3” has >2000 Arbitratily
Adjustable Parameters !
Contrast with quantum mechanics, where there are no arbitrary parameters.
(just particle masses, integral charges & Planck's constant)
e.g.
(unfavorable)
1 e.g.
gauche
C-C-C-C
4
5 e.g.
favorable C … H
“Ideal” Cyclohexane
(by Molecular Mechanics)
Strain
(kcal/mol)
0.33
0.36
Stretch
Bend
0.00
0.00
0.09
Stretch-Bend -0.000
2.15
Easier
2.12
-1.05
(or harder?)
-0.55
4.68
6.32
6.56
TOTAL 7.89
6 gauche butanes
6 0.9 = 5.4
(mnemonic)
Stretches and flattens slightly to reduce VDW
Relaxation of Cyclohexane
(by Molecular Mechanics)
Minimized
0.33
0.36
Stretch
Bend
“Ideal”
0.00
0.00
0.09
Stretch-Bend -0.000
2.15
Torsion 2.12
-1.05
Non-1,4 VDW -0.55
4.68
1,4 VDW 6.32
6.56
TOTAL 7.89
Axial Methylcyclohexane
(by Molecular Mechanics)
H
Axial - Equatorial
8 gauche butanes !
3
[ 2 gauche 2 anti ]
CH
3
Relaxed
0.49
“ A-value ” a measure of group “size”
“Idealized”
Stretch 0.00
0.96
Bend 0.00
0.14
Stretch-Bend -0.00
3.08
Torsion 2.82
-1.31
Non-1,4 VDW 6.12
5.31
1,4 VDW 7.61
8.66
TOTAL 16.55
End of Lecture 33
Dec. 1, 2008
Copyright © J. M. McBride 2009. Some rights reserved. Except for cited third-party materials, and those used by visiting speakers, all content is licensed under a Creative Commons License (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0) .
Use of this content constitutes your acceptance of the noted license and the terms and conditions of use.
Materials from Wikimedia Commons are denoted by the symbol .
Third party materials may be subject to additional intellectual property notices, information, or restrictions.
The following attribution may be used when reusing material that is not identified as third-party content:
J. M. McBride, Chem 125. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 3.0