AP Physics II TEST-Thermodynamics Applications Show all work for
advertisement

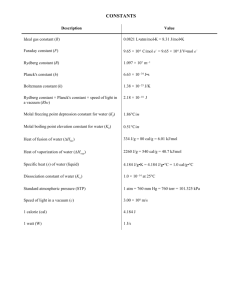
Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________ Period:_____________ AP Physics II TEST-Thermodynamics Applications Show all work for full credit and underline your final answer Rules: (a) Work must be submitted on separate paper. (b) Show all work to include the equation used, conversions must be shown, (c) Include the rearranged formula with values entered, (d) your final answer with units and underlined. Credit will be reduced for missing elements listed above. ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. 2. 3. 4. ____ 5. ____ 6. ____ 7. ____ 8. ____ 9. ____ 10. ____ 11. ____ 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. If it is given that 546 K equals 273C, then it follows that 400 K equals? A temperature change from 15C to 35C corresponds to what incremental change in F? Normal body temperature for humans is 37C. What is this temperature in kelvins? A steel wire, 150 m long at 10C, has a coefficient of linear expansion of 11 106/C. Give its change in length as the temperature changes from 10C to 45C? A rectangular steel plate with dimensions of 30 cm 25 cm is heated from 20C to 220C. What is its change in area? (Coefficient of linear expansion for steel is 11 106/C.) A brass cube, 10 cm on a side, is raised in temperature by 200C. The coefficient of volume expansion of brass is 57 106/C. By what percentage does volume increase? A 2.00-L container holds half a mole of an ideal gas at a pressure of 12.5 atm. What is the gas temperature? (R 0.082 1 Latm/molK) Two moles of nitrogen gas are contained in an enclosed cylinder with a movable piston. If the gas temperature is 298 K, and the pressure is 1.01 106 N/m2, what is the volume? (R 8.31 J/molK) How many atoms are present in a sample of pure iron with a mass of 300 g? (The atomic mass of iron 56 and NA 6.02 1023) Two moles of an ideal gas at 3.0 atm and 10C are heated up to 150 C. If the volume is held constant during this heating, what is the final pressure? What is the root-mean-square speed of chlorine gas molecules at a temperature of 320 K? (R 8.31 J/molK, NA 6.02 1023, and the molecular mass of Cl2 71) What is the internal energy of 50 moles of Neon gas (molecular mass 20 u) at 27C? (R 8.31 J/mol·K) How many calories are equal to one BTU? (One calorie 4.186 J, one BTU 1 054 J.) A 10-kg piece of aluminum (which has a specific heat of 900 J/kgC) is warmed so that its temperature increases by 5.0 C. How much heat was transferred into it? A waterfall is 145 m high. What is the increase in water temperature at the bottom of the falls if all the initial potential energy goes into heating the water? (g 9.8 m/s2, cw 4 186 J/kgC) A 120-g block of copper is taken from a kiln and quickly placed into a beaker of negligible heat capacity containing 300 g of water. The water temperature rises from 15C to 35C. Given cCu 0.10 cal/gC, and cwater 1.00 cal/gC, what was the temperature of the kiln? Find the final equilibrium temperature when 10.0 g of milk at 10.0C is added to 160 g of coffee at 90.0C ? (Assume the specific heats of coffee and milk are the same as water and neglect the heat capacity of the container.) cwater 1.00 cal/g·ºC 4186 J/kg·ºC ____ 18. I take 1.0 kg of ice and dump it into 1.0 kg of water and, when equilibrium is reached, I have 2.0 kg of ice at 0C. The water was originally at 0C. The specific heat of water 1.00 kcal/kgC, the specific heat of ice 0.50 kcal/kgC, and the latent heat of fusion of water is 80 kcal/kg. The original temperature of the ice was? ____ 19. A windowpane is half a centimeter thick and has an area of 1.0 m2. The temperature difference between the inside and outside surfaces of the pane is 15 C. What is the rate of heat flow through this window? (Thermal conductivity for glass is 0.84 J/smC.) ____ 20. The volume of an ideal gas changes from 0.40 to 0.55 m3 although its pressure remains constant at 50 000 Pa. What work is done on the system by its environment? ____ 21. In an isobaric process 4.5 104 J of work is done on a quantity of gas while its volume changes from 2.6 m3 to 1.1 m3. What is the pressure during this process? ____ 22. A system is acted on by its surroundings in such a way that it receives 50 J of heat while simultaneously doing 20 J of work. What is its net change in internal energy? ____ 23. A 4-mol ideal gas system undergoes an adiabatic process where it expands and does 20 J of work on its environment. What is its change in internal energy? ____ 24. A quantity of monatomic ideal gas expands adiabatically from a volume of 2.0 liters to 6.0 liters. If the initial pressure is P0, what is the final pressure? ____ 25. A 5-mol ideal gas system undergoes an adiabatic free expansion (a rapid expansion into a vacuum), going from an initial volume of 10 L to a final volume of 20 L. How much work is done on the system during this adiabatic free expansion? ____ 26. A heat engine exhausts 3 000 J of heat while performing 1 500 J of useful work. What is the efficiency of the engine? ____ 27. A heat engine operating between a pair of hot and cold reservoirs with respective temperatures of 500 K and 200 K will have what maximum efficiency? ____ 28. A heat engine receives 6 000 J of heat from its combustion process and loses 4 000 J through the exhaust and friction. What is its efficiency? ____ 29. A turbine takes in 1000-K steam and exhausts the steam at a temperature of 500 K. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency of this system?