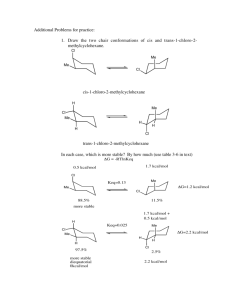
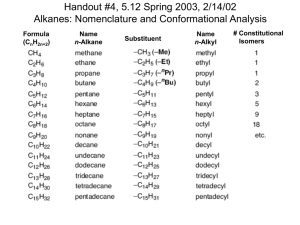
1. Hammes, ch. 1, #1-2a Answer: Write balanced eqn: C6H12O6(s)
advertisement

Enthalpy problems KEY Chem 440 1. Hammes, ch. 1, #1-2a Answer: Write balanced eqn: C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) Æ 2H2O(l) + 6CO2(aq) ∆H°298 = 6*∆H°f(CO2g) + 6*∆H°f(H2O(l)) - 6*∆H°f(O2g) - ∆H°f(C6H12O6(s)) ∆H°298 = 6*(-98.7) + 6*(-68.3) – 6* (0) – (-304.3) ∆H°298 = -697.7 kcal/mol 2. (Taken from Chang, Physical Chemistry for the Chemical and Biological Sciences). Alcoholic fermentation is the process in which carbohydrates are broken down into ethanol and carbon dioxide. The reaction is very complex and involves a number of enzyme-catalyzed steps. The overall change is C6H12O6(s) Æ 2C2H5OH(l) + 2CO2(g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for this reactions, assuming that the carbohydrate is α-Dglucose. Answer: ∆H°298 = 2*∆H°f(C2H5OH(l)) + 2*∆H°f(CO2(g)) - ∆H°f(C6H12O6(s)) ∆H°298 = 2* (-290.76) + 2* (-393.51) – (-1267.11) ∆H°298 = -101.43 kJ/mol 3. (Taken from Tinoco et al., Physical Chemistry) Which of the above two reactions produces more energy per mole of glucose metabolized? What fraction of heat is liberated in the less efficient metabolic pathway? Answer: From 1: ∆H°298 = -697.7 kcal/mol -697.7 kcal/mol * 4.184 kJ/1 kcal = -2919.2 kJ/mol From 2: ∆H°298 = -101.43 kJ/mol So, the reaction in 1 produces more energy. -101.4 = n * -2919.2 n = 0.035 the energy produced in reaction 2 is 3.5% of the energy produced in reaction 1. Enthalpy problems KEY Chem 440 4. (Taken from Tinoco et al., Physical Chemistry) The enzyme catalase efficiently catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to give water and oxygen. At room temperature, the reaction goes essentially to completion. a) Using heats of formation, calculate ∆H°298 for the reaction 2H2O2(g) ' 2H2O(g) + O2(g) ∆H°f for gaseous H2O2 is -133.18 kJ.mol-1 ∆H°f for gaseous H2O is -241.8 kJ.mol-1 Answer: ∆H°298 = 2*∆H°f(H2O(g)) + ∆H°f(O2(g)) – 2*∆H°f(H2O2(g)) ∆H°298 = 2*(−241.8) + (0) − 2∗ (−133.18) ∆H°298 = -217.24 kJ/mol b) The enzyme normally acts on an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide, for which the equation is 2H2O2(aq) ' 2H2O(l) + O2(g) What is ∆H°298 for this process? Answer: ∆H°298 = ∆H°f(O2(g)) + 2*∆H°f(H2O(l)) – 2*∆H°f(H2O2(aq)) ∆H°298 = 0 + 2*(-285.83) – 2*(-191.17) ∆H°298 = -189.3 kJ/mol 5. Hammes, Ch. 1, #1-3 Answer: Balanced equations 2CH3COCOOH(l) + 5O2 Æ 4H2O + 6CO2 2CH3COOH(l) + 4O2 Æ 4H2O + 4CO2 ∆H° = -227 kcal/mol ∆H° = -207kcal/mol reverse the bottom equation and add them to get the desired equation. Must also take negative of sign of heat of combustion for acetic acid, when adding these. So, ∆H° for the oxication of pyruvic to acetic acid is: (-227) + (207) = 20 kcal/mol 6. Hammes, Ch. 1, #1-6 we’ll be looking at this question is class.