How well do you know your functional groups?
advertisement

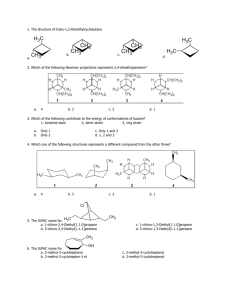
How well do you know your functional groups? Identify the functional group/class of compound for each structure! Alcohol (1o, 2o or 3o?) Aldehyde 1. Alkane 3. NH 2 O H C H3 C 4. CH 3 H3 C CH 3 CH 3 Alkene Alkyne 2. CH2Cl2 5. O 6. H3 C C C H2 Alkyl halide Amide 7. 8. CH3 OH N Amine (1o, 2o, or 3o?) Anhydride OH H 3C H 9. H3C C CH3 10. CH Aromatic Carboxylic acid O 11. C H 3C Cycloalkane CH 3 12. H2 C O C H 3C CH 3 OH CH 3 Diene O 13. Ester 14. C H2 CH Ether SH O 15. 16. H3C Ketone Thiol H2 C H3C 17. O N H CH3 18. O O C O H3C H 3C H C CH 2 OH CH 3 Alkyl groups: (“R”) The hydrocarbon portion of the molecule (CxHy), may vary in size and shape, appearing as chains, rings, or branches. Methyl: -CH3 Ethyl: -CH2CH3 Propyl: -C3H7 n-propyl: H2 C C H2 CH3 CH3 isopropyl: CH CH 3 Butyl: -C4H9 Sec-butyl: Phenyl: C H2 isobutyl: H C H3 C Vinyl: H2 C n-butyl: C H2 CH3 CH 2 Name that alkane! CH3 H-2 C CH3 tert-butyl: CH 3 CH 3 Cyclohexyl: H2 C Allyl: H C C H2 CH3 H3 C C CH Benzyl: H C C H2 CH2 Ortho, meta and para-disubstituted benzene derivatives can be distinguished in the IR by their out of plane bending in the 600-850 cm-1 region. Benzenes with 3 or more substituents require substituent positions be numbered according to the usual IUPAC system (minimize all substituent numbers) Stereochemical configurations and nomenclature: Configuration is based on position of substituent groups or atoms ranked in priority based on Cahn-Ingold Prelog rules (sequence rules) - McMurry Section 5.5 Cis-trans or E/Z stereoisomerism depends on placement of substituent groups on either side of a double bond (cis/trans can also be used with rings) cis or Z = same side trans or E = opposite sides Assign E or Z configuration: Chirality-based stereoisomerism depends on spatial orientation of the substituent groups attached to a chiral carbon - groups are ranked by priority and configurations assigned as R or S Determine whether each structure has the R or S configuration