Blank Formative Assessment
advertisement

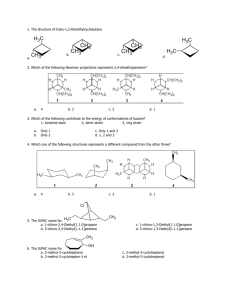
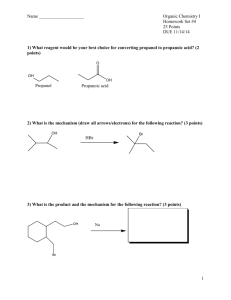
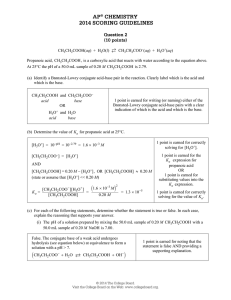
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT: CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS 1. Fill in the missing name or structural formula in the chart below. For letters g-i, fill in both the structural formula and the name of the compound.(2 points each) CH3 H3C O O OH O b. CH3 a. c. pentanoyl chloride d. 3-methyl butanoic anhydride e. (CH3)2CHCCCH2COOH f. CH3COOCH2CH3 2. Arrange the compounds below in order of increasing boiling point: a. pentane b. butanol c. propanol d. butanoic acid _____ < ______ < ______ < _____ e. butanone < _____ 3. Arrange the compounds below in order of solubility in water: a. pentane _____ b. butanol < ______ c. propanol < ______ 4. Draw the structure for aluminum propanoate. < _____ d. butanoic acid < _____ e. butanone 5. Reaction Practice: Draw the structural diagram for each reaction below: a. benzoic acid + sodium hydroxide H+ b. acetic acid + isopropanol H+ c. ethyl methanoate + water d. methyl butanoate + lithium hydroxide e. glycerol + 3 butanoic acid molecules f. 2 propanoic acid (propanoic acid + propanoic acid) g. butanoyl bromide + 1-hexanol 6. Determine the reactants and conditions necessary to produce: O O CH3 a. + H3C OH H2O + H3C OH b. O 7. Use the steps below to write out the reaction mechanism for acetic acid and 2-propanol 1. The carboxyl oxygen of the carboxylic acid is protonated. 2. An alcohol molecule adds to the carbocation produced in Step 1. 3. A proton is lost from the oxonium ion generated in Step 2. 4. A proton is picked up from solution by a hydroxyl group. 5. A pair of unshared electrons from the remaining hydroxyl group helps the water molecule leave. 6. The oxonium ion loses a proton to generate the ester.