Intro to Atoms
advertisement

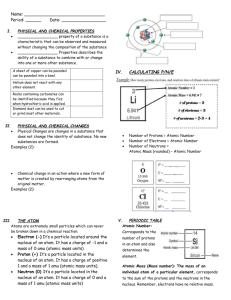
Intro to Atoms Atoms: the basic particle in which all elements are made Nucleus: The central core of an atom containing protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom Laws of Science Law of Conservation of Matter • Matter cannot be created or destroyed Law of Conservation of Mass Established by French Chemist Antoine Lavoisier • In a chemical reaction, the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants. THIS IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT WHEN BALANCING EQUATIONS What’s the MATTER? Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed together, but NOT chemically combined Atomic Models Early Models/Theories of the Atom: Dalton’s Atomic Model: - All matter is composed of atoms - Atoms cannot be made or destroyed - All atoms of the same element are identical - Different elements have different types of atoms - Atoms of 2 or more elements can join together to form a compound Modern Atomic Model – NOT ON YOUR PAPER! • Electrons form a negatively charged cloud around the nucleus • Cannot determine the location of an electron at any given time Atomic Models continued… • • • • • • • JJ Thomson’s Model: Atom is positively charged Discovered Electrons Rutherford’s Model: Protons and the nucleus Electrons orbit around the positively charged nucleus Chadwick’s Model: Discovered neutrons Bohr’s Model: Electrons move in specific layers (shells) Electrons move when atoms absorb or give off energy, moving from one shell to another Atoms and Elements Atomic number • number of protons in an element • Number of electrons the element has Atomic mass: mass of one atom of the element How to calculate neutrons: atomic mass # - atomic number Valence electrons: electrons that can be transferred from one atom to another or may be shared between atoms Chemical symbol: symbol for element (H – Hydrogen) (C – Carbon) Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev • Created first Periodic Table • Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic mass • Placed similar elements in the same group according to their reactions Periods: a horizontal row in the P.T. Groups: vertical columns in the P.T. – also known as families due to similar characteristics Groupings • • • • • • Metals (Alkali , Alkali Earth) Nonmetals Nobel Gases Transition Elements Halogens Common Elements Valence Shells Group 1 = 1 valence electron Group 2 = 2 valence electrons Group 13 = 3 valence electrons Group 14 = 4 valence electrons Group 15 = 5 valence electrons Group 16 = 6 valence electrons Group 17 = 7 valence electrons Group 18 = 8 valence electrons (full shell) Properties of Metals • Classified by its physical properties such as shininess, malleability, ductility, and conductivity. Malleable: can be hammered flat or into other shapes Ductile: can be pulled out into a long wire Conductivity: ability to transfer heat from one object to another Metals continued… Chemical properties: ability of a pure substance to change into another substance. Reactivity: The speed in which an element combines or reacts with other elements Corrosion: the wearing away of metal due to a chemical reaction Metals can be considered an alloy which is a mixture of a metal with one other element (usually found together in nature) Physical and Chemical Properties Physical Chemical • Def: a change that does not result in the formation of any new substances • Examples: Dissolving sugar in water Melting ice cubes Boiling water Crumbling Paper • Def: a change that produces one or more new substances • A chemical reaction will take place • Burning paper • Corrosion • Rusting • Milk or eggs going BAD Nonmetals • • • • • Lack the properties of metals Poor conductors of electricity and heat Reactive with other elements Dull and brittle (break easily) Good insulators Metalloids & Noble Gases Metalloids • Metalloids has characteristics of both metals and nonmetals • Semiconductors: substances that can conduct electricity under some conditions Noble Gases • Unreactive elements • Exist in Earth’s atmosphere