Name: Period: ______ Date: PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL
advertisement
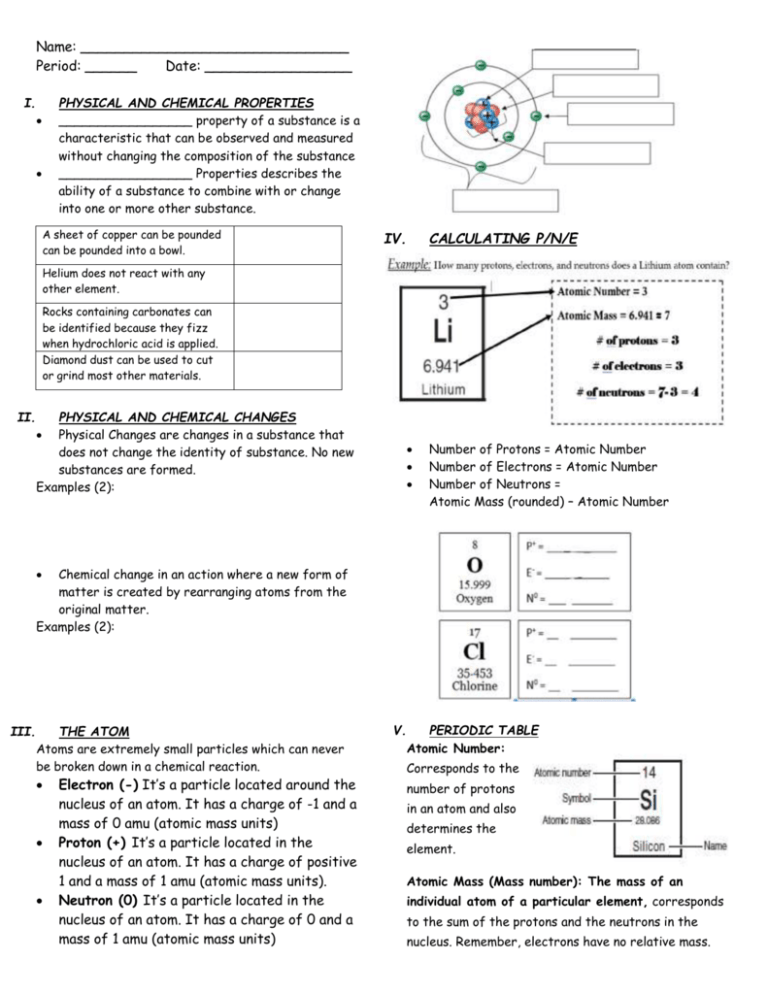
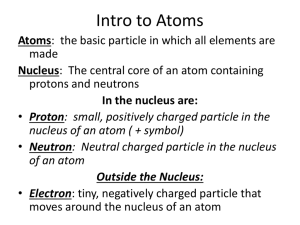
Name: _______________________________ Period: ______ Date: _________________ I. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES _________________ property of a substance is a characteristic that can be observed and measured without changing the composition of the substance _________________ Properties describes the ability of a substance to combine with or change into one or more other substance. A sheet of copper can be pounded can be pounded into a bowl. IV. CALCULATING P/N/E Helium does not react with any other element. Rocks containing carbonates can be identified because they fizz when hydrochloric acid is applied. Diamond dust can be used to cut or grind most other materials. II. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES Physical Changes are changes in a substance that does not change the identity of substance. No new substances are formed. Examples (2): Number of Protons = Atomic Number Number of Electrons = Atomic Number Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass (rounded) – Atomic Number Chemical change in an action where a new form of matter is created by rearranging atoms from the original matter. Examples (2): III. THE ATOM Atoms are extremely small particles which can never be broken down in a chemical reaction. Electron (-) It’s a particle located around the nucleus of an atom. It has a charge of -1 and a mass of 0 amu (atomic mass units) Proton (+) It’s a particle located in the nucleus of an atom. It has a charge of positive 1 and a mass of 1 amu (atomic mass units). Neutron (0) It’s a particle located in the nucleus of an atom. It has a charge of 0 and a mass of 1 amu (atomic mass units) V. PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Number: Corresponds to the number of protons in an atom and also determines the element. Atomic Mass (Mass number): The mass of an individual atom of a particular element, corresponds to the sum of the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus. Remember, electrons have no relative mass. *Symbol: Unique identifier of the element. All elements that have a symbol containing two letters VIII. should capitalize the first letter. VI. METAL, NONMETAL, AND METALLOIDS Metals Are characterized by bright luster, hardness, ability to resonate sound and are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. They are ductile (can be drawn into wire) and malleable (can be beaten into very thin sheets). Non-metals They are non-lustrous, brittle and poor conductors of heat and electricity. Non-metals can be gaseous, liquids or solids. Metalloids Elements that behave like both metals and nonmetals are called metalloids. *Label the periodic table* VII. VALENCE ELECTRONS Electrons on the outermost energy level. Valence electrons are the only electrons that participate in bonding. Boron valence e-= ________ Silicon valence e-= ________ Antimony valance e-= ______ IX. IONS An atom (or group of atoms) that has a positive or negative electrical charge because it has lost or gained electrons. CHEMICAL FAMILIES X. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals Other Nonmetals Other Metals Halogens Noble Gases IONIC CHARGES Atoms tend to lose or gain electrons to attain the electron arrangement of a noble gas.