The Liver cont…..
advertisement

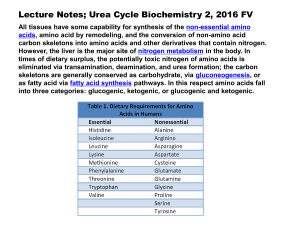
The Liver cont….. • WALT • Amino acids can be deaminated or transaminated • Deamination produces ammonia which is dangerous to the body • Ammonia is converted to urea via the ornithine cycle Transamination • Transamination (or aminotransfer) is the reaction between an amino acid and an alphaketo acid. • The amino group is transferred from the former to the latter; this results in the amino acid being converted to the corresponding α-keto acid, while the reactant α-keto acid is converted to the corresponding amino acid (if the amino group is removed from an amino acid, an α-keto acid is left behind). Transamination • Transamination is accomplished by enzymes called transaminases or aminotransferases. • The human body synthesizes the 10 nonessential amino acids and transamination is the process by which most of these syntheses occur. Deamination • Deamination is the removal of an amine group from a molecule. • In the human body, deamination takes place in the liver. It is the process by which amino acids are broken down. • The amino group is removed from the amino acid and converted to ammonia. The rest of the amino acid is made up of mostly carbon and hydrogen and is recycled or burned for energy. Ammonia • Ammonia is toxic to the human system, and enzymes convert it to urea or uric acid by addition of carbon dioxide molecules in Urea Cycle. • Urea and uric acid can safely diffuse into the blood and then be excreted in urine. • The urea cycle or the ornithine cycle describes the conversion reactions of ammonia into urea. • Since these reactions occur in the liver, the urea is then transported to the kidneys where it is excreted. The overall urea formation reaction is: • 2 Ammonia + carbon dioxide + 3ATP ---> urea + water + 3 ADP