Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry

David L. Nelson and Michael M. Cox
LEHNINGER
PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY
Sixth Edition
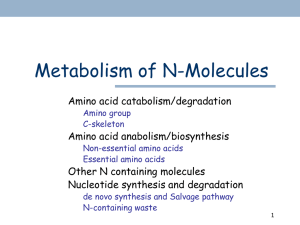
CHAPTER 18
Amino Acid Oxidation and the
Production of Urea
© 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company
Excretion as
Urea
Conversion to: pyruvate acetyl-CoA citric acid cycle intermediates
Digestion by proteases
Digestion by proteases
cytosol mitochondria
NH
4
+
NH
4
+
Forms of excreted nitrogen
Digestion of dietary protein
Protein in stomach stimulates production of hormone gastrin.
Gastrin stimulates secretion of HCl and the protease pepsin.
Pepsin hydrolyzes proteins on amino side of Phe, Trp, Tyr.
In small intestine acidic contents stimulate secretion of the hormone secretin.
Secretin stimulates bicarbonate secretion, bringing pH up to 7.
Amino acids stimulate release of hormone cholecystokinin.
Cholecystokinin stimulates secretion of the proteases: trypsin - hydrolyzes proteins on carboxyl side of Lys, Arg chymotrypsin - carboxyl side of Phe, Trp, Tyr carboxypeptidase A – removes carboxy-terminal amino acids aminopeptidase – removes amino terminal amino acids
cytosol mitochondria
NH
4
+
NH
4
+
Aminotransferases catalyze transfer of amino groups of amino acids to a -ketoglutarate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) functions as an amino group carrier in aminotransferases
Glutamate is transported to the mitochondria where it undergoes oxidative deamination to a -ketoglutarate
cytosol mitochondria
NH
4
+
NH
4
+
Glucose-Alanine
Cycle
Nitrogen excretion and
The Urea Cycle
The Urea Cycle
The citric acid cycle and the urea cycle are linked
The Cost of Urea Synthesis
2 ATPs are used in carbamoyl-phosphate synthesis.
1 ATP is used in arginosuccinate synthesis.
The overall equation for the urea cycle is:
2NH
4
+ + HCO 3+ 3ATP + H
2
O urea + 2ADP + 4Pi + AMP + 5H +
However, fumarate was produced which feeds into the citric acid cycle and is converted to oxaloacetate, producing a molecule of NADH (2.5 ATP)