Cause and Effects of American Revolution
advertisement

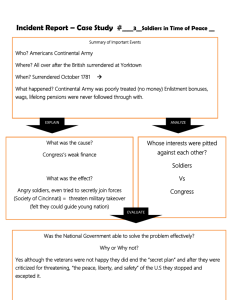
BELL WORK Grab crossword from front desk. Using your resources (i.e. book, internet, blog ppt) complete the crossword. CAUSES OF AMERICAN REVOLUTION 1760s-1776 GEORGIA STANDARDS S S U S H 3 T h e s t u d e n t w i l l e x p l a in t h e p r im a r y c a u s e s o f t h e A m e r ic a n R ev o lut i o n . a . E x p l a i n h o w t h e e n d o f A n g l o - Fr en c h i m p e r ia l c o m p et i t io n a s s e e n i n t h e Fr e n c h a n d I n d i a n Wa r a n d t h e 176 3 Tr e a t y o f P a r i s l a i d t h e g r o un d wo r k f o r t h e A m e r i c a n Rev o l ut i o n . b . E x p l a i n c o l o n i al r e s p o n s e to s u c h B r i t i s h a c t i o n s a s t h e P r o c l am a t i o n o f 176 3 , t h e S t a m p A c t , a n d t h e I n to l e r a b le A c t s a s s e e n i n S o n s a n d D a u g h te r s o f L i b e r t y a n d C o m m i t te e s o f C o r r e s p o n d e nc e . c . E x p l a i n t h e i m p o r t a nc e o f T h o m a s P a i n e ’ s C o m m o n S e n s e to t h e m o ve m e n t f o r i n d e p e n d e nc e . S S U S H 4 T h e s t ud e n t w i l l i d e n t if y t h e i d e o lo g i c a l, m i l i t a r y, a n d d i p l o m a t i c a s p ec t s o f t h e A m e r ic a n R ev o l ut io n . a . E x p l a i n t h e l a n g ua g e , o r g a n i z a t i o n , a n d i n te l l e c t ua l s o u r c e s o f t h e D e c l a r a t i o n o f I n d e p e n d e nc e ; i n c l ud e t h e w r i t i n g o f J o h n L o c ke a n d t h e r o l e o f T h o m a s J e f f e r s o n . b . E x p l a i n t h e r e a s o n f o r a n d s i g n i fi c a nc e o f t h e Fr e n c h a l l i a n c e a n d f o r ei g n a s s i s t a nc e a n d t h e r o l e s o f B e n j a m i n Fr a n k l i n a n d t h e M a r q u i s d e L a f ayet te . c . A n a l y z e G e o r g e Wa s h i n g to n a s a m i l it a r y l e a d e r ; i n c l ud e t h e c r e a t i o n o f a p r o fe s s i o n a l m i l i t a r y a n d t h e l i f e o f a c o m m o n s o l d i er, a n d d e s c r i b e t h e s i g n i fi ca n c e o f t h e c r o s si n g o f t h e D e l awa r e R i v e r a n d Va l l ey Fo r g e . d . E x p l a i n t h e r o l e o f g e o g r a p hy a t t h e B a t t l e o f Yo r k tow n , t h e r o l e o f L o r d C o r nwal l i s , a n d t h e Tr e a t y o f P a r i s , 17 8 3 . FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR (1754-1763) British in debt because of war Begin to tax colonists Thought the colonists should help pay DOCUMENTS OF 1763 Treaty of Paris (1763): ended the French and Indian War and gave British full control over all American colonies Proclamation of 1763: British deal with the Native…Colonists can’t go beyond Appalachian Mountains PROCLAMATION OF 1763 “NO TAXATION WITHOUT REPRESENTATION” England places more taxes without colonists’ approval Sugar Act: (1 st )—sugar and molasses Stamp Act: taxes placed on anything paper (newspapers, licenses, deeds, playing cards) Townshend Acts: glass, paint, etc. Boston Massacre (March 1770): protests of taxes (7 killed by British) NO TAXATION WITH REPRESENTATION RESISTANCE GROUPS The Sons of Liberty—protests against all taxes, damaged British property and started the Boston Tea Party The Daughters of Liberty —protest by boycotts of British cloth (Ladies— make clothes) The Committees of Correspondence—create private communication lines between and amongst the colonies. Thomas Paine—wrote Common Sense (about independence) INTOLERABLE ACTS Punishment for Boston Tea party, Passes Intolerable Acts Closed Boston Harbor (big port in MA) Quartering Act—had to house/feed British soldiers Boston under British military control (Red Coats everywhere) Committees of Correspondence —create 1st Continental Congress Foldable Instructions and notes Today’s foldable! Foldables Follow directions If you need help…ASK Fold, glue, cut Anchor tab=only place where glue goes Things to remember with GLUE • Dot, dot not a lot • One line is just fine Step 1 Cut out the square Make sure not to cut the anchor tab (frame around square) Step 2 Fold along the one of the dotted line “pinch method” Step 3 Cut the dotted lines to the half way point Step 4 Add glue to ANCHOR TAB (inside the frame only place on clean sheet of paper Step 4 Let glue dry then finish cutting the dotted line NOW it’s time for notes! Because Mrs. Cook is so nice……. YOU ONLY HAVE TO WRITE NOTES WHEN YOU SEE SLIDES LIKE THIS!!! John Locke John Locke (1632-1704) Locke describes the natural state of human existence arguing: • …that everyone is born with a natural right to defend his “life, liberty and property”. • …individuals would agree to form a state (i.e. government) that would provide a “neutral judge” to protect the beforementioned rights. • …”all men are created equal.” Thomas Jefferson Principle author of the Declaration of Independence Influenced heavily by Locke and other Enlightenment thinkers Supporter of separation of church and state Slave owner from Virginia Preamble to the Declaration of Independence We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. Declaration of Independence Summer of 1776 the 2nd Continental Congress Philadelphia. Written by Thomas Jefferson include the writing of John Locke and Montesquieu July 4, 1776. The “break-up” between the colonies and Great Britain. Colonists’ grievances to the King. George Washington “Father of the USA” Gained military experience in the French and Indian War. Chosen as Commander in Chief of the Continental Army. One early problem Washington encountered was the creation of a professional military. Washington organized and trained (with the assistance of the French) the various state militias into one “national” army. Life as a common soldier At the urging of Washington, Congress provided for the creation of a standing army. Enlistments were 1-3 years. Pay was meager. Rations were short and the army often have to scavenge to find supplies and food. Disease was common due to close confinement combined with poor diet and sanitation . Washington As a Military Leader Lost a lot battles Believed quick, strong strikes followed by an immediate retreat “hit and run” . This principle is best illustrated when Washington crossed the Delaware River on December 25, 1776 in a surprise attack against British allies. This victory further boosted the morale of the American forces…victory was now strategically possible. Valley Forge Washington’s skill at maintaining his force under trying conditions is best shown during the winter of 1777-78 at Valley Forge, Pennsylvania. The Continental Army was stuck at Valley Forge with very little rations; very little food and insufficient winter attire. However Valley Forge proved to be critical in the further development of the army. Lafayette and other foreign military leaders arrived and trained the soldiers extensively at Valley Forge. This newly trained force would go on to defeat the British at Yorktown 3 years later. Georgia Washington and the Continental Army Washington—commander of Army Created better and trained army Respected though lost many battles Hit-run attack method (Delaware River victory) Soldier life—1-3 years, low pay, lack of food and supplies Valley Forge—cold, 6 months, disease, no food + boot camp Franklin asks France for Help In the 18th century England and France maintained a deep rivalry that played out all over the globe. While the colonial army scored many victories early in the war with England, victory was far from certain. Most Indian tribes were assisting the British who supplied them with high-tech weapons and promised a return of their native lands. At the time of the Declaration, Benjamin Franklin was serving as a diplomat to France. Franklin convinced the French government to lend support to the American rebels against the British. France felt that by supporting the colonial rebellion, they could weaken England militarily and enact revenge for the defeat in the French and Indian War. Marquis de Lafayette Marquis de Lafayette: French General who was an integral part of the American assistance in the Revolution. France supplied money, supplies, troops, weapons, ships, military expertise, etc. Lafayette served alongside General Washington and was influential in the eventual defeat of the British at Yorktown. Statue of Lafayette in D.C French Alliance Ben Franklin convinced the French support to the American rebels against the British. France thought helping would weaken England=revenge for French and Indian War. Marquis de Lafayette—French General France supplied money, supplies, troops, weapons, ships, military expertise, etc. Lafayette fought with General Washington helped at Yorktown. Siege at Yorktown General Lord Cornwallis: British leader who planned to push French-American forces southward in an attempt to divide the Continental Army in two. Cornwallis succeeded…eventually ending up with American forces near the coastal town of Yorktown in Virginia. While awaiting reinforcements from the British navy, the French and Americans were able to corner Cornwallis and his men. Cut off from reinforcements, Cornwallis was forced to surrender effectively ending the American Revolution. Treaty of Paris (1783) The Treaty of Paris (1783) formally ended the American Revolution. The United States won its independence from Great Britain and gained control of land stretching west to the Mississippi River. Next, the newly freed colonists would have the tumultuous task of creating any entirely new government on their own. Victory and the 2nd Treaty of Paris British Lord General Cornwallis—moved south but still close to the sea Battle of Yorktown—British surrounded by the French and Americans British forced to surrender Treaty of Paris 1783—ends the American Revolution • America get independence • Spain gets Florida • France gets African and Caribbean colonies How did the Americans win the war? Auditory Visual Tactile Journal/Diary Fact File (Fact/Opinion 5 facts) Flow Map (artistic map) Comic Strip (6 pics) How-to-book/video News broadcast (script and video)