Present Value Comparison
advertisement

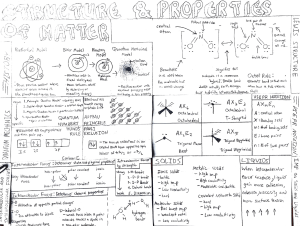
Present Value Comparison Construction Engineering 221 Economic Analysis Present Value Comparison • Present Worth is used to establish a means for comparing projects with different cash flows over different periods. • Discount all future receipts and disbursement to current dollars and choose project with highest worth, or Present Value Present Value Comparison • Can assume interest rate and compare present value or can assume cash flows and compare interest rates (rate of return method) • ROI (return on investment) as used in the book is the same as interest rate • Present worth is the excess present value of one project over another Present Value Comparison • Present value of $100 today is $100 • Present value of $105 you will receive one year from now is $100 (assuming a 5% interest rate • Therefore, the present worth of any investment that does not pay you more than 105 dollars one year from today is zero or less Present Value Comparison • Negative present worth projects use a minimization of loss criteria • Positive present worth projects use a maximization of return on capital criteria • Interest rate used in present worth can be taken from a variety of sources. Most common (conservative) is to use the riskfree rate Present Value Comparison • Calculate the risk free rate from government bond and note auctions (cnnfn.com) Present Value Comparison • Some companies have a hurdle rate or an average annual return rate that they use in their calculations • Can vary the interest rate used based on risk associated with the project (higher risk = higher interest rate) Present Value Comparison • Compound interest is interest earned on principal AND interest earned to date • If interest is paid only on the original investment, then it is simple interest • Simple interest is uncommon in engineering problems, but can apply to certain payouts where interest is paid (literally) each year and the investment is re-started Present Value Comparison • The book uses a trial and error approach to solving ROR problems, but can also interpolate from the tables • Also, many pocket calculators and on-line rate calculators can generate ROR comparisons Present Value Comparison • Example- which of the following options is best: – Option 1 requires $1000 initial investment and pays $120 per year for 10 years – Option 2 requires $2500 initial investment and pays $250 per year for 12 years – General form is P = A (P/A, i, n) Present Value Comparison • Option 1: 1000 = 120 (P/A, i, 10) – (P/A, i, 10) = 8.33, look at n = 10 lines in tables, find i where P/A is closest to 8.33, or i = 3.5% (page 106) – Option 2, same logic, (P/A. i, 12) = 10 (2500/250); look at n = 12 lines for P/A closest to 10, or i = 3% (page 104) Present Value Comparison • Therefore, Option 1 is the best choice, or provides the maximum rate or return FROM AMONG THE AVAILABLE CHOICES • Tomorrow in class- sample problems on ROR and present worth