Porter's Five Forces
advertisement

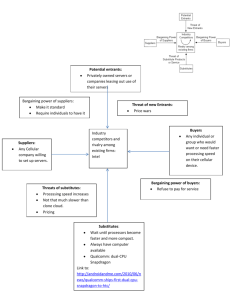
The McIntire Investment Institute Fundamental Presented by Shilpee Raina PORTERS FIVE FORCES: A guide to industry analysis What are Porter’s Five Forces? Developed by HBS professor, Michael Porter: Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining superior Performance Extensive framework utilized to assess an industry’s competitive environment Incredibly useful in determining a company’s positioning and evaluating its strategy The Five Critical Factors Threat of Potential Entrants Bargaining Power of Buyers Bargaining Power of Suppliers Threat of Substitutes Rivalry Among Competitors Apply to: FAST FOOD INDUSTRY Threat of Potential Entrants • Ability of new firms to successfully enter the market due to level of BARRIERS TO ENTRY – Economies of scale, capital requirements, cost & distribution advantages: International Food Chains – Product or service differentiation: Happy Meals – Psychological factors: Burger King brand name • Fast Food Industry: HIGH barriers to entry, LOW threat of entrants Bargaining Power of Buyers The buyers ability to drive down prices, demand higher quality goods, and play competitors against each other Power GAINED by: High concentration of Buyers relative to companies: several fast eating options for mainstream consumer Products/services are undifferentiated: burgers are burgers Purchases represent significant fraction of buyer’s cost: fast food is inexpensive, lower buying anxiety Bargaining Power of Buyers Power REDUCED by: Differentiate Product or Services by raising SWITCHING COSTS: chalupas, happy meals, whoppers Avoid dependence on one buyer: kids, teens, and adults Fast food industry: HIGH Bargaining Power of Buyers Bargaining Power of Suppliers The suppliers ability to raise prices, or reduce quantity and quality of inputs Power GAINED by: Supplier’s industry is concentrated: input foods are common goods Buyer is not important to supplier: several food chains No substitutes: numerous food wholesalers Power REDUCED by: Supply flexibility: relationships with many wholesalers Backward integration: develop own farms Fast Food Industry: LOW Threat of Substitutes These are products/services that perform the same function, but are in different industries: grocery stores, fast casual Availability of substitutes limits industry profitability To REDUCE threat: Product/service differentiation: dollar menus, brands Collective industry response: healthier foods, low prices Fast Food Industry: HIGH Rivalry Among Competitors Competition is intensified when: Competitors are numerous and equally balanced Slow industry growth: fast food is saturated High fixed costs: need to sell high volumes to recup Standardized products/services: intense price competition, $1 menus Fast Food Industry: HIGH level of rivalry In Summation Fast Food Industry is highly competitive due to: high barriers to entry, high bargaining power of suppliers, significant substitutes, and intense rivalry. QUESTIONS?